Detecting glaucoma early is critical to preventing irreversible vision loss. Known as the "silent thief of sight," glaucoma often progresses without noticeable symptoms until significant damage has occurred. Thankfully, glaucoma detection tests have advanced significantly, offering a better chance of early diagnosis and effective management.
What Is Glaucoma?
Glaucoma refers to a group of eye conditions that damage the optic nerve, often due to high internal eye pressure. Left unchecked, this damage can lead to permanent vision loss or blindness. Common types of glaucoma include primary open-angle glaucoma (the most prevalent) and angle-closure glaucoma, which can cause sudden vision problems.
Several factors increase your risk, including age, family history, and medical conditions like diabetes or hypertension. Treatment options, such as glaucoma treatment, can help control the disease if identified early. Regular eye exams, especially for at-risk individuals, are crucial.
Why Early Detection Matters
The absence of early symptoms in glaucoma makes routine screenings incredibly important. Early diagnosis can help slow progression and save vision by starting treatments such as eye drops, laser therapy, or surgery.
Advanced testing techniques now allow ophthalmologists to detect glaucoma much earlier than before. Here are the most effective advanced eye tests for glaucoma that you should know about.
Advanced Eye Tests for Glaucoma
1. Tonometry (Eye Pressure Test)
Tonometry measures intraocular pressure within your eyes. High pressure is a significant risk factor for glaucoma. During this painless test, your eye doctor uses a special instrument to lightly press against your eye. Normal eye pressure ranges between 10 to 21 mm Hg, and anything above this threshold could indicate potential problems.
Pro Tip: Relax during this test and avoid holding your breath, as tension can affect accuracy.
2. Visual Field Testing
This test checks for blind spots in your peripheral and central vision. Your doctor may ask you to press a button whenever you notice a light in your peripheral view. Results can indicate areas of the sight already affected by glaucoma.
Advice: Repeat visual field tests periodically to monitor changes, especially if you're diagnosed with or at risk for glaucoma.
3. Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT)
OCT imaging is one of the most reliable tools for an early glaucoma diagnosis. This non-invasive scan captures detailed, cross-sectional images of the retina and optic nerve. It helps track thinning in the retinal nerve fiber layer, a hallmark of glaucoma.
For further information on OCT imaging, visit the National Eye Institute.
4. Gonioscopy
Gonioscopy determines whether the angle where the iris meets the cornea is open or closed. This information identifies whether you have open-angle or angle-closure glaucoma. After numbing your eyes, the doctor places a small lens on your cornea to examine the angle.
5. Pachymetry
Pachymetry measures corneal thickness. A thinner-than-average cornea can indicate a higher risk of developing glaucoma, while an abnormally thick cornea could lead to false-positive pressure readings.
6. Dilated Eye Exam
By dilating the pupil with eye drops, doctors can examine the back of the eye. This test gives a detailed view of the retina and optic nerve, allowing for the detection of subtle signs of optic nerve damage.
Also Read: How Environmental Factors Are Impacting Your Eyes and What You Can Do About It
How Often Should You Get Tested?
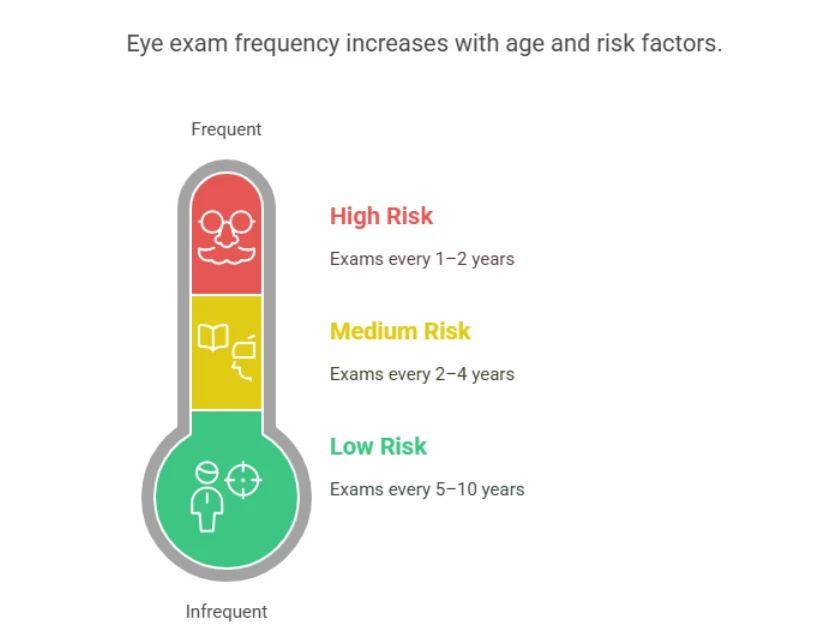
Your age and risk factors dictate the frequency of eye exams:
- Ages 20–39: Every 5–10 years (low risk), more often if at risk
- Ages 40–64: Every 2–4 years
- Ages 65 and above: Every 1–2 years
If there's a family history of glaucoma or if you experience symptoms like eye pain, blind spots, or sudden vision loss, schedule a comprehensive exam immediately.
The Role of Technology in Early Detection
Modern technologies like high-tech imaging systems are reshaping glaucoma diagnostics. For example, combined structure-function indices (CSFI) pool data from visual tests and imaging tools to predict glaucoma progression more accurately. These techniques reduce diagnostic uncertainty and increase the likelihood of catching glaucoma at its earliest stages.
You can explore how advanced facilities like the Advanced Eyecare Center integrate these cutting-edge diagnostic tools for precise and timely care.
Key Takeaway on Early Diagnosis:
Detecting glaucoma in its early stages not only preserves vision but can also make treatments more effective and less invasive. Advanced testing technologies such as OCT imaging and tonometry are life-changing tools for this purpose.
Myths About Glaucoma Testing
- Myth: "I don’t have symptoms, so I don’t need testing."
- Fact: Most forms of glaucoma show no symptoms until substantial damage has occurred.
- Myth: "Glaucoma is untreatable."
- Fact: While it isn’t curable, treatments are highly effective in halting progression if caught early.
Final Note
A proactive approach to eye health dramatically reduces the risk of vision loss from glaucoma. By scheduling regular exams and opting for glaucoma detection tests, including advanced diagnostics, you empower yourself to detect the condition at its earliest stages.
Pro Tip: Never skip your routine eye exams. Glaucoma can affect anyone, but early diagnosis can make all the difference in preserving your vision.
Invest in your eye health. Book an appointment with a qualified ophthalmologist and ask about advanced eye tests for glaucoma. Early action is your best defense!