Organizations must move to the cloud if they want to increase app performance, have scalability, and be cost-effective. However, because the majority of apps are not initially created as cloud-native, moving programs to the cloud is a challenging process. This approach is fraught with difficulties and problems, including application reworks, security holes, and unforeseen costs. To make the transition to the cloud go smoothly, substantial planning is required.
Because cloud providers offer consistent pay-as-you-go pricing, scalability, or flexibility, historically, businesses have desired to shift their applications to the cloud. They now desire conditions that encourage innovation.
What is Application Migration?
Moving software programs from one computing environment to another is referred to as application migration. This can involve moving applications from one data centre to another, from a public to a private cloud, or from an organization’s internal server to the environment of a cloud provider.
Applications are frequently created for a single cloud platform or to function in a specific environment on a specific operating system. As a result, transferring an application to a different setting can be difficult.
Businesses may access the public cloud while maintaining the privacy of their data thanks to hybrid cloud environments, which include the characteristics of both public and private cloud environments. Companies can use the flexibility and computing power of the public cloud for straightforward and non-sensitive computing tasks, while still keeping business-critical apps and data on-site and safely secured behind a company firewall.
Even within the same environment, different apps will require various routes to the cloud.
How to create your Application Migration Strategy?
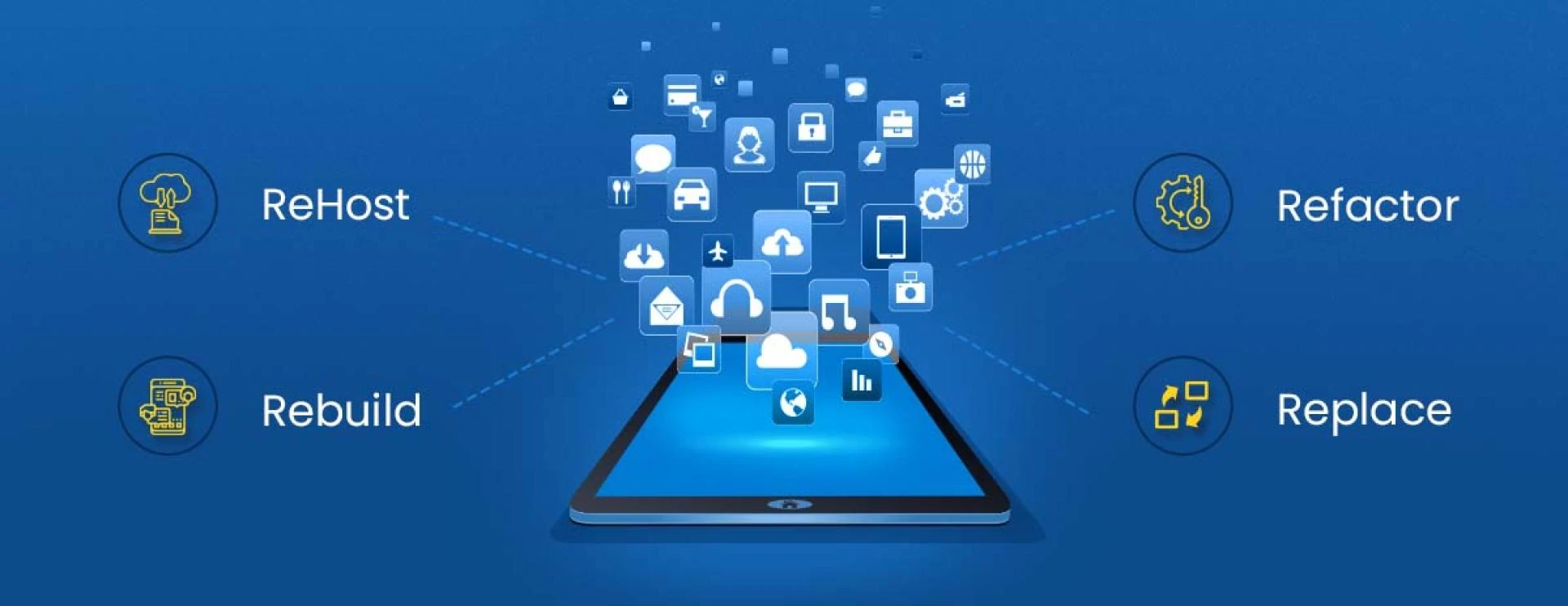

For your organization, the best application migration strategies are the 5Rs: Re-host, Refactor, Revise, Rebuild, and Replace. These 5 R’s stand for the following:
Re Host
Re-hosting is a primary step in application migration which entails moving your organization’s current apps from their on-site configuration to the cloud. The process of copying and pasting your programs from your setup onto the cloud is what it is, in the simplest words. As you are simply moving the program without making any alterations, this is the simplest option with the lowest risk. Because businesses do not have to worry about operational and infrastructural expenditures, this technique is also cost-effective.
Refactor
Re-architecting or refactoring entails converting an application into a cloud-native application and necessitates a comprehensive rewrite of the application to accommodate the cloud environment in case of application migration. Organizations that seek to improve their infrastructure and apps to increase agility can employ this method. Developers that want to test new applications while utilizing the benefits of cloud environments may find this to be a useful tactic.
Rebuild
Prior to considering a cloud migration, redundant applications must be found. This tactic necessitates that businesses, and developers in particular, completely rewrite an application. When an application does not align with shifting technical trends or corporate objectives, rebuilding should be taken into consideration. It’s crucial to get rid of any existing applications that don’t provide enough value for your company to justify their expenditures. Your development teams may benefit from these cost savings by producing more effective and practical apps.


