Have you experienced a nagging pain in the gums, just around the root of the tooth?
This must be a tooth abscess! An abscess is simply a collection of infected fluid around the root of the tooth. The abscess has a spongy feeling when touched and can be quite painful at an advanced stage. In order to understand the formation of a tooth abscess, it is important to know the cause.
What is a Tooth Abscess?When there is a puncture to the tissue complex on the gums around the tooth, it serves as a doorway for the microbes in the mouth. As these microbes accumulate within the pocket, around the root of the tooth, they stagnate and become infected. This is a tooth abscess.
An abscess is a collection of infection fluid that forms as a result of bacteria infiltrating tissue complex after an injury. A dental abscess can be detected near the root of a tooth. To comprehend the formation of a dental abscess, it is essential to first know what caused it.
How does a Tooth Abscess Occur?
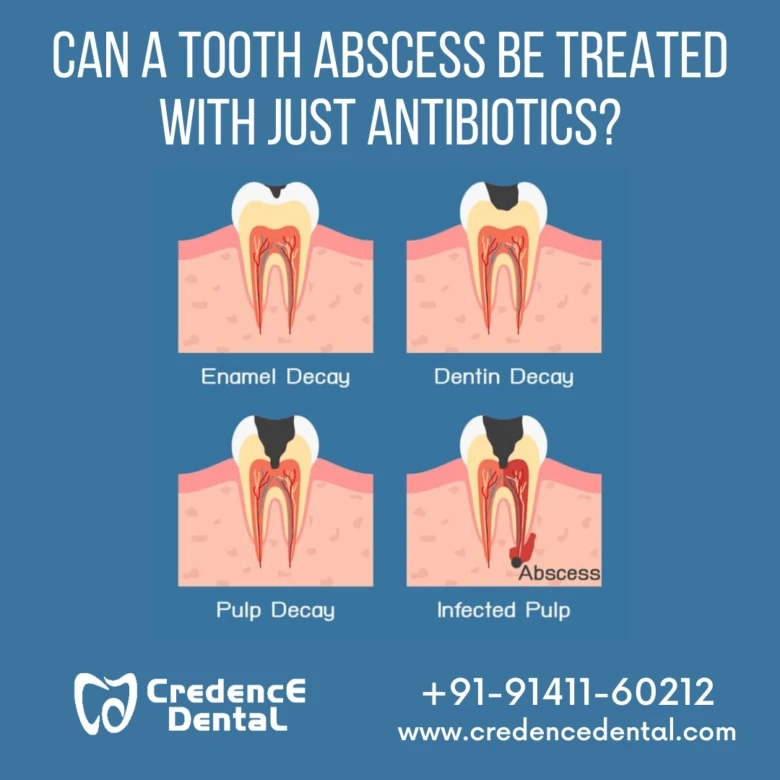
If oral hygiene precautions are not followed, microorganisms might find their way onto the tooth’s surface. These microorganisms have the ability to release acids that can eat away at the tooth’s hard tissue layers (enamel and dentin). When a tooth begins to deteriorate, the deeper the decay is, the more painful it becomes. The enamel and dentin protect the pulp, which is located at the center of the tooth. When the decay reaches the pulp, the pain intensifies as the nerves and blood vessels in the pulp feel it. The microorganisms infect the entire pulpal chamber, and the pulp in the roots becomes infected very quickly.
The microorganisms present in abscessed teeth can easily survive in the presence or absence of oxygen. Apart from cavities/rotting, the microorganisms can also create an abscess through a tooth that has had previous treatment but has not been fully sealed or a tooth that has been cracked. Hence, it’s critical to get rid of the harmful microbes. This is done by root canal treatment being performed by a dentist.
Antibiotic therapy in combination with dental treatment
When a patient arrives with swelling, discomfort, and redness around the tooth, an abscess must be drained. The abscess is cleared by drilling a hole in the tooth and allowing the abscess to drain. The root canals are irrigated with liquid medications that eliminate all of the debris and biofilms left behind by the bacteria. A medicament is administered within the canals to prevent the tooth from becoming infected again. The dentist will advise the patient to take antibiotics for 3 to 5 days during the course of this procedure, which can be finished in a single sitting or span up to three sessions.
Antibiotics for dental abscesses are ones that target a wider spectrum of germs and have no or minimal side effects when consumed. Some of the most commonly prescribed treatment modalities for controlling the spread and eradicating the microbes include amoxicillin, metronidazole, cephalosporins, and clindamycin. The dosage for each one of them differs depending on the pharmacological effects they have on the body. Antibiotics are prescribed to the patient based on their age and the presence or absence of a systemic illness and history of drug allergy.
Can antibiotics only treat dental abscess?
If a patient visits the dentist with an abscess, just prescribing antibiotics will not provide a long-term treatment. The swelling may subside temporarily, and the patient may believe that his or her condition has improved. However, because the abscess’s core cause has not been treated entirely, the microorganisms may get a base on the decaying, fractured, or exposed surfaces of the teeth, resulting in a re-infection.
Does antibiotic therapy help with tooth abscess pain?
When a tooth abscess is diagnosed and treated promptly, it has a very good prognosis. If left untreated, the abscess might spread to the surrounding teeth, resulting in septicemia. Certain areas of the face may get infected and bloated, necessitating the scheduling of procedures to drain them. Antibiotics are effective at preventing the spread of bacteria. However, they should never be used as the only means of removing an abscess. As a result, a visit to the dentist is needed upon the occurrence of a dental abscess.
What are the possible treatment options to treat dental abscess?
RCT, Incision and drainage or both with oral or IV antibiotics.Extraction, if abscess does not respond to RCT/Incision and drainageComplications of dental Abscess
Space infection involving multiple tissue spaces around head and neckLudwig’s AnginaOsteomyelitisSepticemiaCall us or Whatsapp us or book an appointment