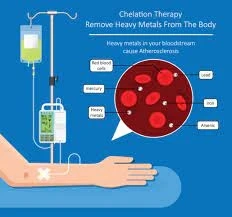
Chelation therapy, a medical procedure gaining traction in recent years, involves the administration of chelating agents to remove heavy metals and toxins from the body. The term \'chelation\' is derived from the Greek word \'chele,\' meaning claw—a fitting metaphor for the way chelating agents bind to metals and facilitate their elimination. The best EDTA oral chelation therapy has garnered attention for its potential in treating conditions associated with metal toxicity. In this blog, we will delve into the primary purposes and procedures of chelation therapy.
Purposes of Chelation Therapy
- Metal Detoxification: One primary purpose of chelation therapy is to eliminate toxic heavy metals from the bloodstream. Exposure to these metals can occur through environmental pollutants or occupational hazards. You can also buy chelation therapy drugs that can be administered orally and bind to the metals, eliminating these substances from the body.
- Cardiovascular Health: Chelation therapy has been explored as an alternative treatment for cardiovascular diseases. It is believed that removing excess calcium deposits from arterial walls may enhance blood flow, potentially reducing the risk of heart-related issues.
- Treatment for Metal Poisoning: Chelation therapy is a recognised medical intervention for acute metal poisoning. When an individual is exposed to high levels of toxic metals, such as iron or arsenic, chelating agents help to neutralise and eliminate these substances from the body.
Procedures of Chelation Therapy
- Administration of Chelating Agents: The procedure involves the intravenous administration of chelating agents, such as ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA). These agents circulate through the bloodstream, binding to heavy metals and forming compounds that can be excreted out of the body.
- Monitoring and Adjusting Dosages: The healthcare provider closely monitors the patient during the chelation therapy session, adjusting the dosage of chelating agents based on individual response and tolerance. Regular monitoring ensures the effectiveness of the treatment while minimising potential side effects.
- Multiple Sessions for Optimal Results: Chelation therapy typically requires multiple sessions to achieve optimal results. The number of sessions depends on the specific health concerns being addressed and the severity of metal toxicity. You can also try the best EDTA oral chelation therapy, which is done orally to help eject metals from the body.
Conclusion
Chelation therapy is a versatile approach, targeting heavy metal detoxification, cardiovascular health, and metal poisoning. At the same time, it is essential to approach this therapy with caution, particularly in non-traditional uses, as ongoing research unveils potential benefits and risks. It is also vital to address metal-related risks. For heavy metals, chelation therapy is imperative. Alternatively, for smaller metals, one can buy chelation therapy drugs, offering oral solutions to the problem.