Electrophoresis is a powerful tool in protein analysis. When you probe into the world of scientific research, understanding the differences between 2D Electrophoresis and SDS-PAGE can greatly impact the accuracy and efficiency of your experiments. In this blog post, we will explore the distinct techniques offered by Kendrick Labs, shedding light on the nuances of each method and guiding you towards making informed decisions for your protein analysis needs.
Principles of Protein Analysis
Overview of Electrophoresis
One of the fundamental techniques in protein analysis is electrophoresis, a method used to separate proteins based on their size and charge. Electrophoresis relies on the principle that charged molecules will move in an electric field towards the opposite charge. 2D electrophoresis and SDS-PAGE are two common electrophoretic techniques used by Kendrick Labs to analyze proteins.
Importance of Protein Separation
For accurate protein analysis, it is crucial to separate proteins from complex samples to study them individually. Protein separation allows you to identify different proteins, determine their relative abundance, and investigate post-translational modifications. Precise separation of proteins is important for understanding protein function, interactions, and cellular pathways.
Proteins are diverse molecules with unique structures and functions, making it necessary to separate them based on their properties for detailed analysis. Through techniques like 2D electrophoresis and SDS-PAGE, Kendrick Labs can offer comprehensive protein analysis services that can facilitate your research goals and provide valuable insights into the proteome of interest.
2D Electrophoresis
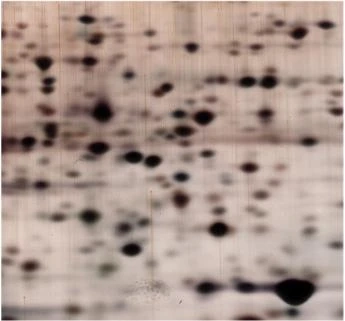
There's a powerful analytical technique utilized in protein research called 2D Electrophoresis. This method allows you to separate complex protein mixtures based on their isoelectric point and molecular weight, providing a comprehensive view of the protein composition in a sample.
Definition and Principle
With 2D Electrophoresis, proteins are first separated based on their isoelectric point in the first dimension using isoelectric focusing (IEF). Then, the proteins are separated in the second dimension based on their molecular weight using SDS-PAGE. This two-step process results in a 2D gel where each protein appears as a distinct spot, allowing for precise identification and quantification.
Limitations of 2D Electrophoresis
With 2D Electrophoresis, there are limitations such as the potential loss of low abundance proteins during the complex separation process. Additionally, the technique can be time-consuming and labor-intensive, requiring a high level of expertise to ensure accurate results.
Advantages: Despite its limitations, the power of 2D Electrophoresis lies in its ability to provide detailed information on protein expression patterns and modifications, enabling researchers to uncover critical insights into biological processes.
SDS-PAGE
Definition and Principle
For the SDS-PAGE technique, the acronym SDS stands for sodium dodecyl sulfate. SDS is an anionic detergent used to denature proteins and provide a uniform negative charge, allowing for separation based purely on molecular weight. The principle behind SDS-PAGE is straightforward: the proteins are separated in a polyacrylamide gel based on their size.
Advantages of SDS-PAGE
To begin with, one of the key advantages of SDS-PAGE is its ability to provide highly accurate molecular weight determination for proteins. Furthermore, this technique offers excellent resolution, allowing you to separate proteins that differ in size by as little as one kilodalton.
The precise molecular weight determination achieved through SDS-PAGE is advantageous when you need to confirm the purity of a protein sample or analyze protein complexes. Additionally, this method is widely used in research laboratories due to its reliability and reproducibility.
Comparison of 2D Electrophoresis and SDS-PAGE
Many laboratories use either 2D electrophoresis or SDS-PAGE for protein analysis. These techniques have their strengths and weaknesses, and choosing the right one depends on your specific research needs. Here, we will compare 2D electrophoresis and SDS-PAGE in terms of resolution and sensitivity, sample preparation and handling, as well as cost and time efficiency.
For quick and cost-effective protein analysis, SDS-PAGE is often the preferred choice. It offers a balance between efficiency and simplicity, making it ideal for everyday research tasks. On the other hand, if your research demands higher resolution and sensitivity, and you are willing to invest more time and resources into sample preparation, 2D electrophoresis may provide the insights you need for your experiments.
Applications of 2D Electrophoresis and SDS-PAGE
Proteomics Research
On your journey through proteomics research, both 2D electrophoresis and SDS-PAGE play vital roles in understanding the complexity of protein mixtures. 2D electrophoresis helps you separate thousands of proteins based on both charge and size, providing a detailed map of the proteome. On the other hand, SDS-PAGE is crucial for analyzing individual proteins, determining their molecular weights, and assessing purity.
Technical Considerations
Instrumentation and Equipment
To ensure accurate results in both 2D electrophoresis and SDS-PAGE, you must have the appropriate instrumentation and equipment. For 2D electrophoresis, a specialized apparatus is needed due to the two-dimensional separation process involving isoelectric focusing and SDS-PAGE. On the other hand, SDS-PAGE requires a simpler setup with a vertical or horizontal gel electrophoresis system and power supply.
Gel Preparation and Staining
An necessary step in both techniques is gel preparation and staining. To achieve optimal protein separation in 2D electrophoresis, you must prepare immobilized pH gradient (IPG) strips for isoelectric focusing, followed by SDS-PAGE. Staining methods such as Coomassie blue or silver stain are commonly used for visualizing protein bands. With SDS-PAGE, the process involves casting a polyacrylamide gel and adding SDS to denature the proteins for uniform migration.
For 2D electrophoresis, the staining process can be more time-consuming due to the two-step separation method, but it provides a higher resolution for complex protein mixtures. In contrast, SDS-PAGE offers a quicker and simpler staining procedure, making it ideal for routine protein analysis in the laboratory.
Data Analysis and Interpretation
On completion of electrophoresis, the next crucial step is data analysis and interpretation. In 2D electrophoresis, specialized software is often used to analyze the complex protein patterns resulting from the two-dimensional separation. Image analysis tools help identify protein spots, quantify spot intensities, and compare protein expression levels between samples.
A key difference between the two techniques lies in the complexity of data analysis. 2D electrophoresis generates a vast amount of data due to the separation in two dimensions, requiring sophisticated software for accurate interpretation. On the other hand, SDS-PAGE provides simpler band patterns, making it easier to visualize and analyze protein migration.
Summing up
Hence, after analyzing the information provided by Kendrick Labs comparing 2D electrophoresis and SDS-PAGE for protein analysis, you have gained a deeper understanding of these two techniques. Both methods have their advantages and limitations, with 2D electrophoresis offering better resolution and separation of complex protein mixtures, while SDS-PAGE provides a simpler and quicker analysis of individual proteins.
By considering the specific requirements of your research or project, you can now make a more informed decision on which technique to utilize for protein analysis. Remember to carefully evaluate the sensitivity, resolution, cost, and time constraints of each method to ensure that you achieve accurate and reliable results for your scientific endeavors.