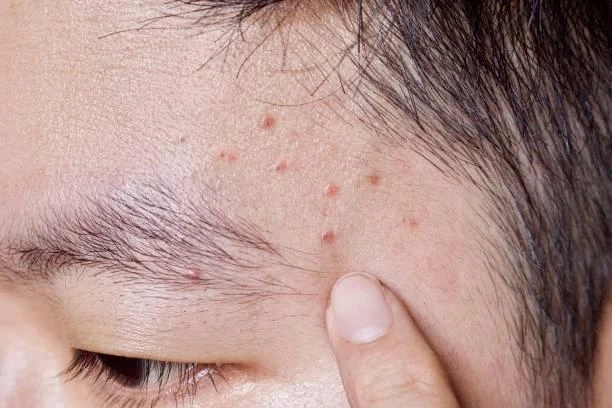
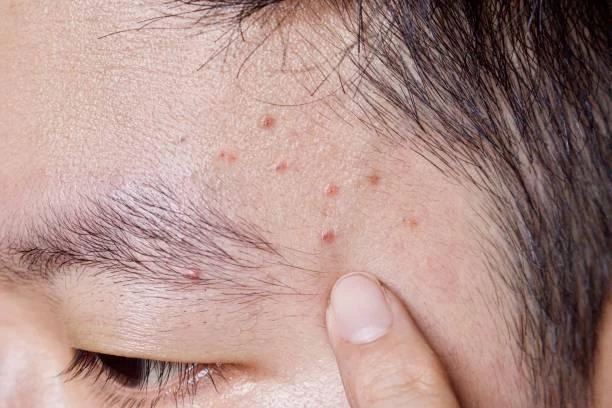
 Folliculitis, derived from the Latin word "folliculus," meaning "small bag," is a common skin condition characterized by the inflammation of hair follicles. While it is typically not a serious condition, folliculitis can be uncomfortable and may cause aesthetic concerns for those affected. In this article, we delve into the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for folliculitis to comprehensively understand this dermatological issue.
Folliculitis, derived from the Latin word "folliculus," meaning "small bag," is a common skin condition characterized by the inflammation of hair follicles. While it is typically not a serious condition, folliculitis can be uncomfortable and may cause aesthetic concerns for those affected. In this article, we delve into the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for folliculitis to comprehensively understand this dermatological issue.
Causes of Folliculitis:
Folliculitis can occur for various reasons, and the underlying cause often determines the type and severity of the condition. Common causes of folliculitis include bacterial, fungal, or viral infections. Staphylococcus aureus is a bacterium commonly associated with folliculitis, while fungal infections are often attributed to the overgrowth of yeast, such as Malassezia species. Additionally, certain viruses, such as the herpes simplex virus, can lead to viral folliculitis.
Other contributing factors to folliculitis include:
- Trauma or Friction: Shaving, waxing, or wearing tight clothing can irritate hair follicles, leading to inflammation and folliculitis.
- Blockage of Hair Follicles: Excessive oil production, sweat, or the use of occlusive skincare products can clog hair follicles, creating an environment conducive to bacterial or fungal growth.
- Weakened Immune System: Individuals with compromised immune systems, such as those with HIV/AIDS or undergoing chemotherapy, may be more susceptible to developing folliculitis.
- Hot and Humid Environments: Warm and moist conditions promote bacterial and fungal growth, increasing the risk of folliculitis, especially in areas where sweat accumulates, such as the groin or armpits.
Symptoms of Folliculitis:
The symptoms of folliculitis vary depending on the underlying cause and severity of the condition. Common signs and symptoms include:
- Red, Pus-filled Bumps: Affected areas may develop small red bumps resembling pimples or acne. These bumps may be tender or itchy and can contain pus.
- Itching or Burning Sensation: Folliculitis can cause discomfort, including itching or a burning sensation, particularly when the affected area is irritated or inflamed.
- Localized Pain or Tenderness: In some cases, folliculitis may be accompanied by pain or tenderness, especially when pressure is applied to the affected area.
- Clusters of Bumps: Folliculitis often appears in clusters or patches, particularly in areas where hair follicles are present, such as the scalp, face, neck, chest, back, buttocks, or thighs.
- Scarring or Hyperpigmentation: Severe or recurrent cases of folliculitis may lead to scarring or changes in skin pigmentation, particularly if the condition is not properly treated.
Treatment Options for Folliculitis:
The treatment of folliculitis depends on the underlying cause and severity of the condition. Mild folliculitis cases may resolve independently without medical intervention, while more severe or recurrent cases may require treatment to alleviate symptoms and prevent complications. Common treatment options for folliculitis include:
- Topical Antibiotics: For bacterial folliculitis, topical antibiotics such as mupirocin or clindamycin may be prescribed to reduce inflammation and eliminate bacterial infection.
- Antifungal Medications: To eradicate fungal overgrowth and relieve symptoms, fungal folliculitis may be treated with antifungal medications, such as clotrimazole or ketoconazole.
- Topical Steroids: In cases of severe inflammation, topical steroids may be prescribed to reduce redness, itching, and swelling associated with folliculitis. However, prolonged use of steroids should be avoided due to the risk of skin thinning and other adverse effects.
- Antiviral Medications: Viral folliculitis caused by herpes simplex virus may require antiviral medications, such as acyclovir or valacyclovir, to suppress viral replication and alleviate symptoms.
- Warm Compresses: In cases of bacterial folliculitis, applying warm compresses to the affected region can alleviate discomfort and encourage the pus-filled bumps to drain.
- Avoidance of Irritants: Individuals with folliculitis should avoid shaving, waxing, or using harsh skincare products that may further irritate or inflame hair follicles.
- Good Hygiene Practices: Good hygiene, including regular skin cleansing with mild soap and water, can help prevent the recurrence of folliculitis and promote healing.
- Medical Procedures: In severe or recurrent cases of folliculitis, medical procedures such as laser therapy, photodynamic therapy, or drainage of abscesses may be recommended to address underlying causes and prevent complications.
Preventing Folliculitis:
While folliculitis may not always be preventable, certain standards can help reduce the risk of developing the condition:
- Maintain Good Hygiene: Regularly cleanse the skin with mild soap and water, particularly after sweating or engaging in activities that may irritate hair follicles.
- Avoid Tight Clothing: Wear loose-fitting clothing made of breathable fabrics to reduce friction and lessen the risk of folliculitis, especially in areas prone to sweating.
- Practice Safe Shaving: Use sharp, clean razors and shaving cream to minimize irritation and prevent cuts or nicks that can lead to folliculitis.
- Moisturize Dry Skin: Keep the skin well-moisturized to prevent dryness and irritation, which can exacerbate folliculitis.
- Limit Exposure to Hot and Humid Environments: Avoid prolonged exposure to hot tubs, saunas, or humid environments, as these conditions can promote bacterial and fungal growth on the skin.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions) About Folliculitis:
- Can folliculitis be contagious?
Folliculitis caused by bacterial or fungal infections can potentially be contagious, especially if there is direct skin-to-skin contact or sharing of contaminated items such as towels or razors. Practicing good hygiene and avoiding sharing personal objects is essential to decrease the risk of spreading folliculitis to others. However, not all cases of folliculitis are contagious, particularly those caused by non-infectious factors such as trauma or irritation.
- Is folliculitis the same as acne?
While folliculitis and acne share some similarities in terms of appearance, they are distinct skin conditions with different underlying causes. Folliculitis involves the inflammation of hair follicles, typically caused by bacterial, fungal, or viral infections, as well as other factors such as trauma or friction. Acne is mostly caused by hair follicles getting clogged with extra oil, dead skin cells, and bacteria. This blockage can lead to the creation of comedones like blackheads, whiteheads, pimples, and cysts. Though both conditions may show up as red bumps or pustules on the skin, the treatments can differ. It\'s vital to seek guidance from a healthcare expert for a correct diagnosis and suitable care plan.
Conclusion
In summary, folliculitis is a prevalent skin issue marked by hair follicle inflammation, usually triggered by bacterial, fungal, or viral infections. Although usually not severe, folliculitis can lead to discomfort and aesthetic worries for individuals experiencing it. Understanding the underlying causes, symptoms, and available treatment methods for folliculitis is important to address the condition and avoid complications effectively. By maintaining good hygiene practices, steering clear of irritants, and seeking prompt medical care when needed, individuals can lower their chances of developing folliculitis and keep their skin healthy.