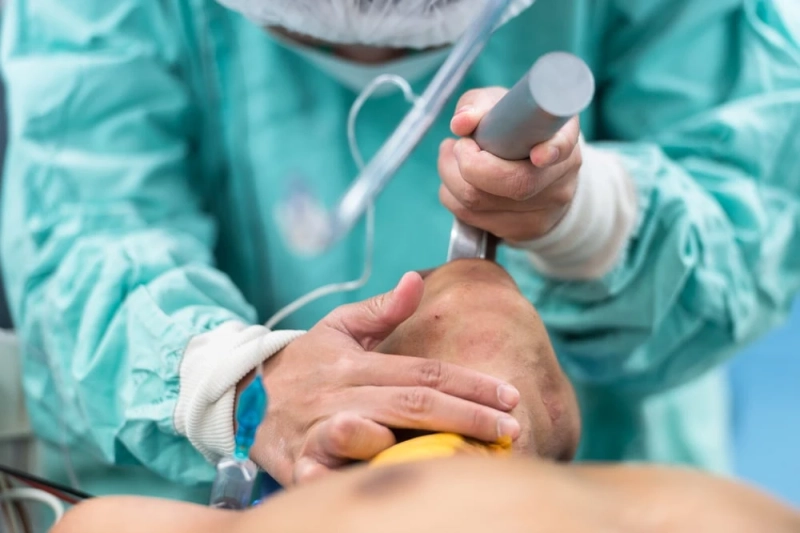
The windpipe, or trachea, is a tube that connects the larynx to the bronchi of the lungs. The trachea transports air from the upper respiratory tract (throat and larynx) to the bronchi. Endotracheal tubes are hollow, flexible plastic tubes that are placed from the mouth to the trachea when a person is unable to breathe on his or her own. The endotracheal tubes are linked to a ventilator, which supplies enough oxygen to the patient. Endotracheal intubation is the process of inserting an endotracheal tube (EI). Endotracheal tubes come in a variety of styles, including cuffed, uncuffed, and reinforced.
An inflatable cuff surrounds a cuffed endotracheal tube, which is used to provide an airway through the trachea while also preventing aspiration of foreign materials such as saliva or vomitus into the bronchus.
An uncuffed endotracheal tube is a flexible plastic tube that is inserted through the patient's mouth into the trachea to assist breathing. The endotracheal tube is linked to a ventilator, which supplies oxygen to the lungs. Endotracheal tubes that have been reinforced or armored are more flexible and resistant to blockage. The flexibility is achieved by embedding a spiral of wire into the wall of the endotracheal tube, which provides both strength and flexibility. Other endotracheal tube types include laser-resistant endotracheal tubes, double-lumen tubes, bronchial blockers, and micro laryngeal tubes.
Read more @ https://bit.ly/3H13FGN
0