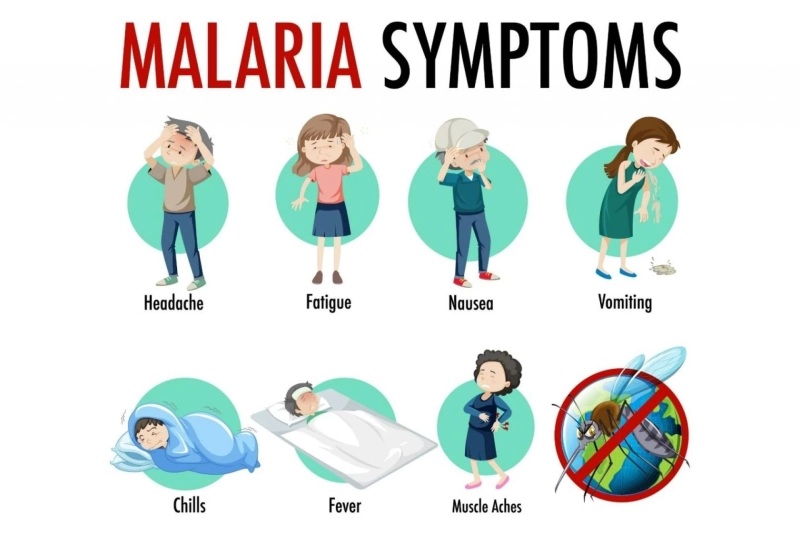
Malaria Disease Overview:
Malaria Disease is a life-threatening mosquito-borne disease caused by the Plasmodium parasites. It is transmitted to humans through the bites of infected female Anopheles mosquitoes. With a significant global health burden, malaria predominantly affects tropical and subtropical regions. Sub-Saharan Africa bears the highest malaria burden, followed by Southeast Asia and parts of the Americas. This disease poses a substantial challenge to healthcare systems worldwide.
Since millions of individuals continue to encounter malaria symptoms each year, public health initiatives should place a high focus on malaria prevention and treatment. While market actors make contributions through product development and innovation, government programs are crucial in fostering awareness, research, and development in these fields.
The Market Competitors Listed Below are Revolutionizing Healthcare with Innovative Diagnostic Inventions:
Thermo Fisher ScientificBio-Rad LaboratoriesRoche DiagnosticsQiagenAgilent TechnologiesBioneer CorporationOthersThe Market Competitors Listed Below are Revolutionizing Healthcare with Innovative Diagnostic Inventions:
NovartisCiplaGlaxoSmithKline (GSK)AR Scientific, IncMedicef Pharma(WRAIR)RocheIpca LaboratoriesSanofiDiagnostic Analysis:
Accurate diagnosis is paramount for effective malaria management. Conventional diagnostic methods include microscopy and rapid diagnostic tests (RDTs). Microscopy involves examining blood smears for the presence of Plasmodium parasites, while RDTs detect specific malaria antigens. Recent advancements in molecular techniques, such as Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR), have enhanced diagnostic accuracy, particularly in cases of low parasitemia.
Treatment Analysis:
Artemisinin-based combination therapies (ACTs) are the frontline treatments for uncomplicated Plasmodium falciparum malaria, the most deadly species. Other species, like P. vivax and P. ovale, require different treatment regimens, often including primaquine to prevent relapses. However, the emergence of drug-resistant strains, especially in Southeast Asia, poses a significant challenge to malaria control efforts.
Competitive Analysis:
The pharmaceutical landscape for antimalarial drugs is evolving, with several major players investing in research and development. Established pharmaceutical companies, as well as research institutions and NGOs, are collaborating to develop novel treatments and vaccines. Public-private partnerships like the Medicines for Malaria Venture (MMV) are crucial in advancing antimalarial drug development.
Browse More Information:
https://www.diseaselandscape.com/infectious/malaria-disease-market-entry-strategy-overview
Regulatory Framework:
Regulatory bodies, such as the World Health Organization (WHO) and national health agencies, play a pivotal role in setting guidelines for malaria control and treatment. They oversee drug approvals, provide treatment protocols, and monitor resistance patterns. The WHO's Global Malaria Programme (GMP) sets global policies and strategies for malaria prevention and control.
Clinical Assessment:
Clinical evaluation of malaria encompasses a range of parameters including fever, parasite density, anemia, and organ dysfunction. Severe malaria cases necessitate intensive care and prompt treatment to prevent fatal outcomes. Monitoring for complications like cerebral malaria, severe anemia, and acute respiratory distress syndrome is crucial.
Market Trends Analysis:
The malaria therapeutics market has seen notable growth in recent years, driven by increased funding for research and development, heightened awareness, and improved access to healthcare in endemic regions. Additionally, the introduction of novel antimalarial drugs and promising vaccine candidates is shaping the market dynamics.
Regional Insights:
Malaria incidence varies significantly by region. Sub-Saharan Africa bears the highest burden, with children under five and pregnant women being particularly vulnerable. Southeast Asia experiences a significant prevalence of drug-resistant strains. The Americas, particularly parts of South America, continue to combat the disease, albeit with varied success.
Conclusion:
Malaria remains a pressing global health challenge, demanding concerted efforts in research, treatment, and prevention. Advances in diagnostics, treatments, and collaborations between public and private sectors are pivotal in the fight against this deadly disease. Effective implementation of regulatory policies and continued surveillance are critical to curbing malaria's impact worldwide.
Browse Through More Infectious Diseases Research Reports.
Related Reports:
Insights and Trends in the Global Landscape of Lung Cancer Services
The symptoms, transmission, and precautions of Monkeypox
The Myths of Pneumonia: Symptoms, Causes, and Prevention Methods
Navigating the Complex Autoimmune Disorder of Lupus
Ringworm Comprehensive Guide: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment