Introduction:
Melasma is a common skin condition characterized by patches of dark discoloration on the face, particularly on the cheeks, forehead, and upper lip. While melasma is not harmful, it can be distressing for those affected. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and available treatment options is essential for effectively managing this condition and achieving clearer skin. In this article, we will explore the causes, symptoms, and effective treatment options for melasma.
What Causes Melasma?
Melasma Treatment in Abu Dhabi occurs when there is an overproduction of melanin, the pigment responsible for skin color. Several factors can contribute to the development of melasma, including:
Hormonal Changes: Fluctuations in hormone levels, such as those experienced during pregnancy, oral contraceptive use, or hormone replacement therapy, can trigger melasma.
Sun Exposure: Ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun stimulates melanocytes, the cells that produce melanin, leading to increased pigmentation in the skin.
Genetic Predisposition: Individuals with a family history of melasma are more likely to develop the condition themselves.
Symptoms of Melasma:
The primary symptom of melasma is the presence of dark, irregularly shaped patches on the face. These patches typically appear on areas of the skin that are exposed to the sun, such as the cheeks, forehead, bridge of the nose, and upper lip. Melasma patches may vary in size and can range from light brown to grayish-brown or dark brown in color. The patches may also become more pronounced with sun exposure or hormonal changes.
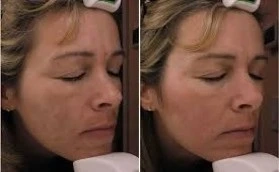
Effective Treatment Options for Melasma:
While melasma can be challenging to treat, several treatment options can help improve the appearance of dark patches and even out skin tone:
Topical Treatments:
Hydroquinone: A skin-lightening agent that inhibits melanin production and reduces the appearance of dark spots.
Retinoids: Vitamin A derivatives that promote cell turnover and fade pigmentation.
Azelaic Acid: A naturally occurring acid that reduces melanin production and helps even out skin tone.
Chemical Peels:
Glycolic Acid Peels: Chemical peels containing glycolic acid can exfoliate the skin and improve the appearance of melasma.
Trichloroacetic Acid (TCA) Peels: TCA peels penetrate deeper into the skin, targeting more severe cases of melasma.
Laser Therapy:
Fractional Laser Therapy: Laser treatments can target melanin deposits in the skin, breaking them down and reducing pigmentation.Microneedling:
Microneedling: This procedure involves creating tiny punctures in the skin with fine needles, stimulating collagen production and reducing pigmentation.Preventive Measures for Melasma:
Preventing melasma from worsening or recurring involves taking steps to protect the skin from further sun damage:
Sun Protection: Wearing broad-spectrum sunscreen with a high SPF, seeking shade, and wearing protective clothing and accessories can help prevent sun-induced melasma flare-ups.
Hormonal Management: For individuals whose melasma is triggered by hormonal changes, consulting with a healthcare provider about hormone-related triggers and adjusting medication or contraceptive methods if necessary may be beneficial.
Conclusion:
Melasma can be a challenging condition to manage, but with the right approach, it is possible to improve the appearance of dark patches and achieve clearer, more even-toned skin. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and available treatment options for melasma, individuals can take proactive steps to address this common skin concern and feel more confident in their skin.