Introduction
Choosing between PDM vs PLM is a critical decision for businesses involved in product design, engineering, and manufacturing. Both Product Data Management (PDM) and Product Lifecycle Management (PLM) systems are designed to manage product-related information, but they serve distinct functions. This blog explores the differences, benefits, and best use cases for PDM vs PLM to help you determine the right solution for your organization.
Understanding PDM
What is PDM?
Product Data Management (PDM) is a system that focuses on handling product-related data, primarily design and engineering files. It ensures data accuracy, security, and accessibility for teams working on product development.
Key Features of PDM
- Centralized File Storage – Stores CAD models, drawings, and documents in a structured manner.
- Version Control – Prevents data conflicts by ensuring teams work with the latest design iterations.
- User Access Control – Restricts or grants permissions based on roles.
- Seamless CAD Integration – Works directly with software like SolidWorks and AutoCAD.
- Quick Search and Retrieval – Enhances productivity by reducing time spent searching for files.
Why Businesses Use PDM
Companies that rely on complex design and engineering processes use PDM to streamline collaboration and prevent costly errors caused by mismanaged data.
Understanding PLM
What is PLM?
Product Lifecycle Management (PLM) is a more comprehensive system that manages the entire lifecycle of a product from ideation to retirement. Unlike PDM, which focuses on design files, PLM integrates engineering, manufacturing, supply chain, compliance, and market strategies into a unified workflow.
Key Features of PLM
- End-to-End Product Management – Covers everything from concept development to product disposal.
- Cross-Department Collaboration – Connects design, production, marketing, and sales teams.
- Compliance Management – Ensures adherence to regulatory and industry standards.
- Supply Chain Integration – Helps manage suppliers, vendors, and material sourcing.
- Process Automation – Reduces manual work and enhances efficiency.
Why Businesses Use PLM
Organizations looking for full product lifecycle control implement PLM to enhance innovation, quality, and time-to-market while ensuring compliance with industry regulations.
PDM vs PLM: A Comparative Analysis
While both PDM vs PLM systems manage product data, their scope and functionalities are distinct.
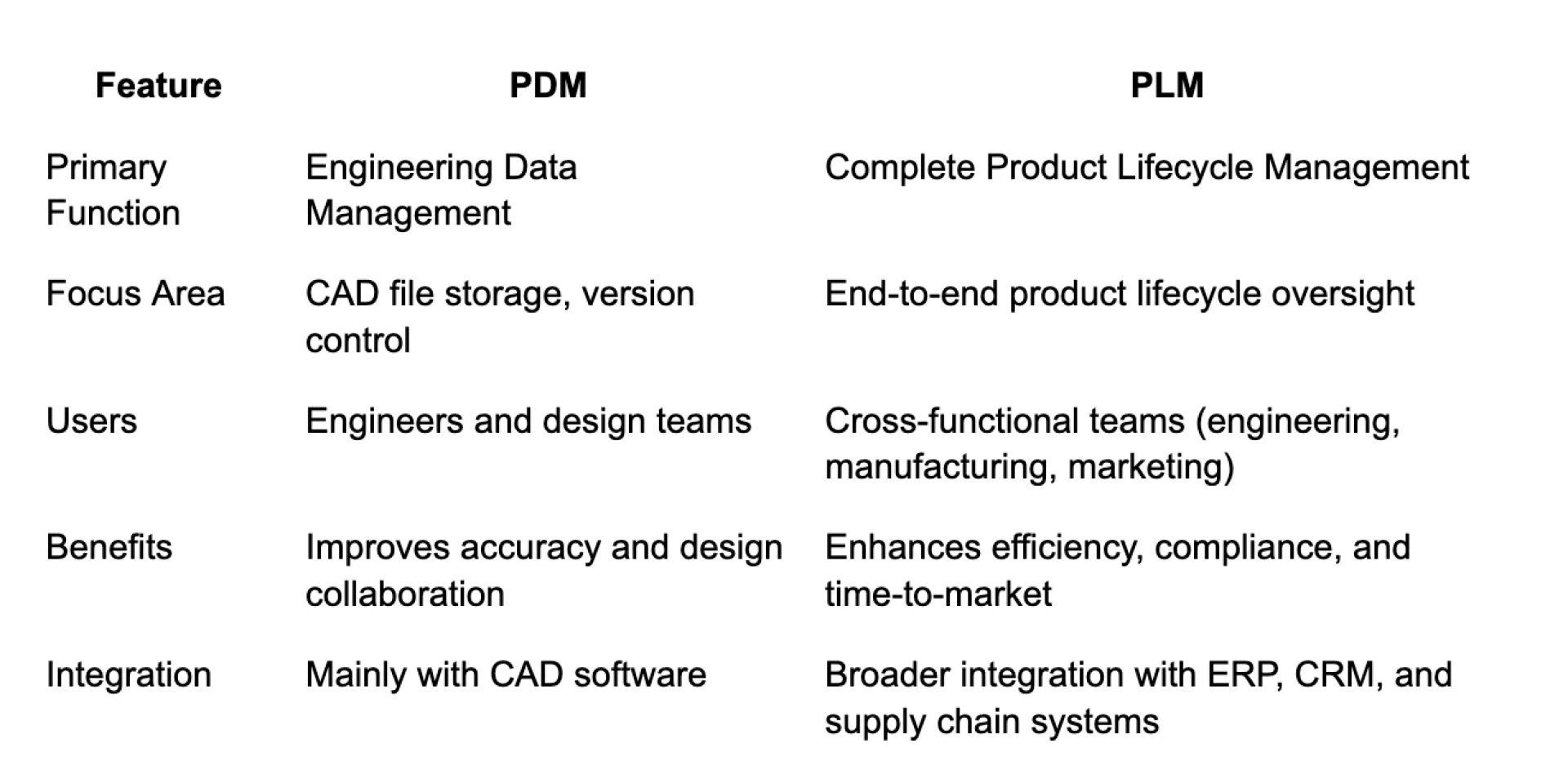
Advantages of Implementing PDM and PLM
Understanding PDM vs PLM helps organizations make the best decision for their needs. Below are key benefits:
Benefits of PDM
- Enhances Design Integrity – Prevents version conflicts and lost files.
- Improves Collaboration – Ensures engineers work on the latest designs.
- Reduces Rework and Errors – Eliminates design inconsistencies.
- Saves Time on File Searches – Organized storage speeds up access to critical documents.
Benefits of PLM
- Holistic Product Management – Aligns product design, development, and commercialization.
- Facilitates Cross-Departmental Coordination – Integrates teams from different domains.
- Accelerates Time-to-Market – Automates key processes to enhance efficiency.
- Ensures Compliance and Standardization – Helps meet regulatory and quality standards.
PDM vs PLM: Which One Should You Choose?
Deciding between PDM vs PLM depends on your company’s needs.
- If your primary goal is managing CAD files, revisions, and design collaboration, PDM is the right choice.
- If you need a system to track the entire product lifecycle, including supply chain and compliance, PLM is the better option.
- Many organizations start with PDM and later expand to PLM as their business grows.
Industries That Benefit from PDM and PLM
Both PDM vs PLM have applications across various industries:
Automotive
- PDM ensures design consistency and version control.
- PLM helps manage supply chains, regulatory approvals, and production planning.
Aerospace
- PDM secures CAD files and technical documentation.
- PLM assists in compliance with strict aviation regulations.
Consumer Electronics
- PDM organizes PCB layouts and electronic schematics.
- PLM oversees product lifecycle from R&D to market launch.
Conclusion
The PDM vs PLM debate is crucial for businesses looking to optimize product development. PDM is ideal for companies focusing on design data management, while PLM provides a broader framework for managing products from inception to retirement. Organizations should evaluate their operational needs and scalability when choosing between PDM vs PLM.
FAQs
1. What is the key difference between PDM and PLM?
PDM focuses on managing engineering data, while PLM manages the entire product lifecycle from ideation to disposal.
2. Can a company use both PDM and PLM?
Yes, many businesses use PDM for engineering data management and later adopt PLM for full lifecycle management.
3. Is PLM necessary for small businesses?
While PLM is more common in large enterprises, small businesses can also benefit from its collaborative and process optimization capabilities.
4. How does PDM integrate with CAD software?
PDM integrates with popular CAD tools like SolidWorks, AutoCAD, and CATIA, ensuring design data is well-organized and accessible.
5. Which industries benefit the most from PDM and PLM?
Industries such as automotive, aerospace, consumer electronics, and medical devices benefit significantly from PDM vs PLM by optimizing data management and production workflows.
By understanding PDM vs PLM, companies can make informed decisions to improve efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance product success.

