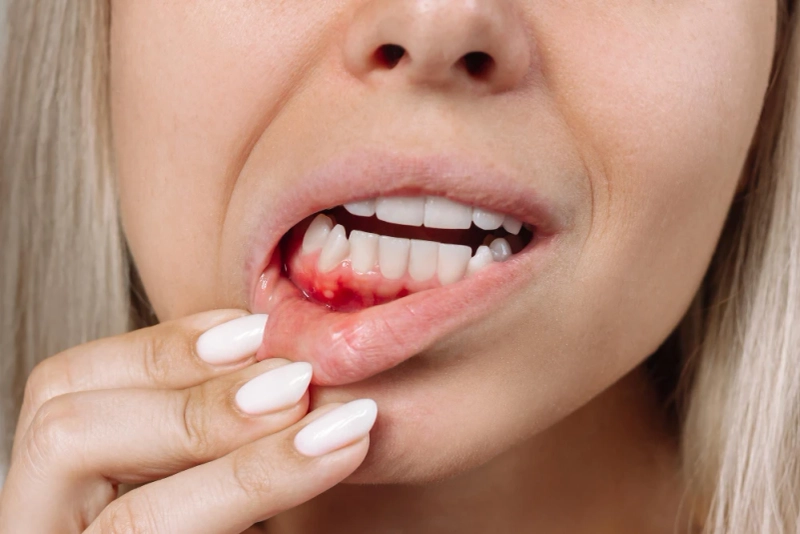
Gum bleeding may be a sign of serious dental health problems that should not be disregarded. While minor bleeding during brushing or flossing is normal, chronic bleeding gums may be a sign of an underlying issue that requires medical treatment. We'll look at a few of the most typical reasons why people get bleeding gums in this blog post and talk about what you can do to keep your mouth healthy.
Poor Oral Hygiene:
It is important to take gum bleeding seriously as it could indicate more significant dental health issues. While some bleeding occurs naturally when you brush or floss, persistent bleeding gums could indicate a more serious problem that needs to be treated by a doctor. In this blog post, we'll examine some of the most common causes of bleeding gums and provide preventative measures for maintaining oral health.
Gingivitis:
The first stage of gum disease, known as gingivitis, is characterised by red, swollen, and bleeding gums. It is typically brought on by bad oral hygiene practices that let plaque accumulate along the gum line. Fortunately, gingivitis is curable with frequent dental cleanings, professional teeth cleanings, and good oral hygiene practices.
Periodontitis:
Gingivitis can develop into periodontitis, a more severe form of gum disease, if treatment is not received. When gums recede from teeth due to periodontitis, pockets of bacteria-filled tissue occur. Gum recession, tooth loss, and chronic bleeding gums are all possible outcomes of the infection spreading and harming the tissues and bones that support the teeth.
Hormonal Changes:
Hormonal changes, including those that happen after menopause, puberty, or pregnancy, might make gum inflammation and bleeding more likely. These hormonal fluctuations may exacerbate pre-existing gum disease or lead to the development of new gum problems by increasing the gums' sensitivity to plaque and germs.
Medications:
Gum bleeding can be made more likely by taking certain drugs, including immunosuppressants, blood thinners, and antihypertensives. Gums can bleed more easily as a result of certain medications because they can weaken gum tissue or interfere with blood coagulation systems. This is especially true while brushing or flossing.
Vitamin Deficiencies:
Vitamin C and vitamin K deficiency in particular can weaken gums and increase bleeding risk. These are important vitamins and nutrients. Vitamin K is involved in blood clotting, while vitamin C is essential for collagen synthesis and gum health.
Ill-Fitting Dental Appliances:
Inadequately fitting braces, dentures, or other dental appliances can aggravate the gums and result in bleeding. Dental appliances must fit correctly and be changed as necessary since persistent pressure or friction on the gum tissues can cause irritation and tissue damage.
Tobacco Use:
Gum disease and bleeding gums can be greatly increased by smoking or using other tobacco products. Smokers are more prone to oral health difficulties because tobacco use impairs immunity, lowers blood flow to the gums, and hinders the body's natural healing and tissue-repair processes.
Conclusion:
While occasional bleeding gums may not always be cause for alarm, persistent or severe bleeding should prompt a visit to your dentist for evaluation and treatment. Maintaining good oral hygiene practices, including brushing twice a day, flossing daily, and scheduling regular dental check-ups, is essential for preventing gum disease and keeping your gums healthy. By understanding the common causes of bleeding gums and taking proactive steps to address them, you can protect your oral health and enjoy a confident smile for years to come.