As the world grapples with the pressing need for sustainability, the spotlight is increasingly falling on oleochemicals as a key component of the solution. Derived from natural fats and oils, oleochemicals offer an environmentally friendly alternative to traditional petrochemicals. Their versatility and biodegradability make them essential in a wide range of applications, from personal care products to industrial lubricants. This article explores how oleochemicals are shaping a more sustainable future across various sectors.
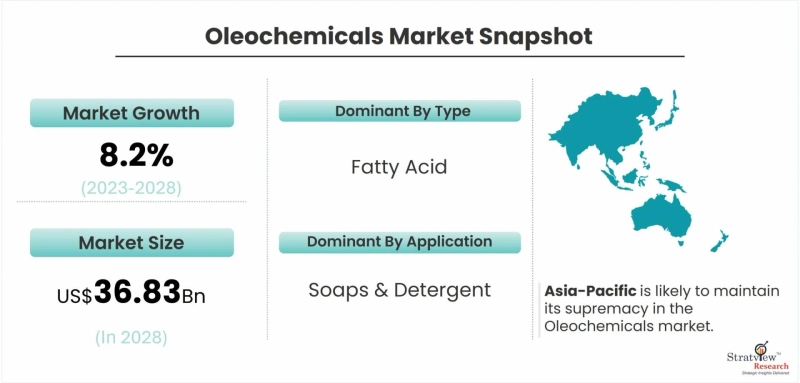
According to Stratview Research, the oleochemicals market was estimated at USD 22.89 billion in 2022 and is likely to grow at a CAGR of 8.2% during 2023-2028 to reach USD 36.83 billion in 2028.
What Are Oleochemicals?
Oleochemicals are chemical compounds obtained from natural sources such as plant oils and animal fats. The primary types of oleochemicals include fatty acids, glycerol, fatty alcohols, and methyl esters. These substances are fundamental building blocks in many products, providing a greener alternative to petrochemical-based materials.
The Role of Oleochemicals in Sustainability
Renewable Resources: Unlike petrochemicals, which are derived from finite fossil fuels, oleochemicals come from renewable resources. Plants such as palm, soybean, and coconut oil can be cultivated and replenished, ensuring a sustainable supply chain.
Biodegradability: Oleochemicals are inherently biodegradable, breaking down into harmless substances that do not persist in the environment. This property is crucial in reducing pollution and mitigating the environmental impact of chemical products.
Lower Carbon Footprint: The production and use of oleochemicals typically result in lower greenhouse gas emissions compared to petrochemicals. This reduction in carbon footprint is a significant step toward combating climate change.
Applications of Oleochemicals in Sustainable Products
Personal Care and Cosmetics: The beauty industry is increasingly turning to oleochemicals to formulate sustainable and skin-friendly products. Natural soaps, shampoos, lotions, and creams often contain oleochemicals that provide moisturizing properties and are gentle on the skin.
Food and Beverage: In the food industry, oleochemicals serve as emulsifiers, stabilizers, and preservatives. They help maintain the texture, flavor, and shelf life of food products while ensuring they remain safe and natural.
Pharmaceuticals: Oleochemicals are used in pharmaceuticals to create biodegradable and biocompatible drug delivery systems. They improve the efficacy of medications and reduce the environmental impact of pharmaceutical waste.
Industrial Applications: Oleochemicals are used in the production of biodegradable lubricants, solvents, and coatings. These products are essential in reducing the environmental footprint of industrial operations and promoting sustainable practices.
Innovations and Future Trends in Oleochemicals
Advanced Biotechnology: Advances in biotechnology are enabling the development of new and improved oleochemical products. Genetic engineering and microbial fermentation are being used to produce oleochemicals more efficiently and with enhanced properties.
Circular Economy: The concept of a circular economy, where waste is minimized, and resources are reused, is gaining traction. Oleochemicals fit well into this model, as they can be derived from agricultural by-products and waste oils, promoting resource efficiency.
Green Chemistry: Green chemistry principles are driving the development of safer and more sustainable chemical processes. Oleochemicals play a central role in this movement, offering alternatives that are less toxic and more environmentally friendly.
Collaborative Efforts: Industry collaborations and partnerships are fostering innovation in the oleochemicals market. Companies are working together to develop new technologies and applications, accelerating the adoption of sustainable solutions.
Challenges and Opportunities
While the oleochemicals market presents numerous opportunities for sustainability, it also faces challenges. Issues such as the deforestation associated with palm oil production and competition with food crops for agricultural land need to be addressed. Sustainable sourcing practices, certification schemes, and investment in alternative feedstocks are crucial in overcoming these challenges.
Conclusion
Oleochemicals are at the forefront of the shift toward sustainable solutions in the chemical industry. Their renewable nature, biodegradability, and lower environmental impact make them a key component in the transition to a greener future. As innovation continues to drive the development of new oleochemical applications, their role in promoting sustainability across various sectors will only grow. By embracing oleochemicals, industries can reduce their environmental footprint and contribute to a more sustainable world.