The term is credited to author Neal Stephenson, who coined it in his 1992 science fiction novel Snow Crash, in which he imagined realistic-looking digital avatars inhabiting virtual reality environments. In a technical sense, the "metaverse" is synonymous with the Internet of Everything (IoE), or "Internet of Everything", a concept born in the early 2000s that eventually became a less ambitious version of itself, the Internet of Things (Internet of Things, IoT).
Since then, milestones have been achieved on the road to a true metaverse, an online virtual world incorporating augmented reality, virtual reality, 3D holographic avatars, video, and other media. As it expands, the metaverse will offer a hyper-real alternate world, or what comic book fans would call a "parallel universe." But this description talks only about the frontend, or user experience of an application, without explaining the backend: the engine that makes it works. To understand the back room of this new fictional universe we must take a different perspective.
A Different Perspective on the Metaverse
“The metaverse brings together people, processes, data, and things (real and virtual) to make networking more valuable than ever. It brings information to the plane of action to create new capabilities, richer experiences and unprecedented economic opportunities for companies, people and countries.
In its simplest formulation, the metaverse would be the intelligent interconnection between people, processes, data and things. It would be a world in which billions of objects have sensors to detect measure and assess their status. All of them would be interconnected through public or private networks, with standardized or specific protocols.
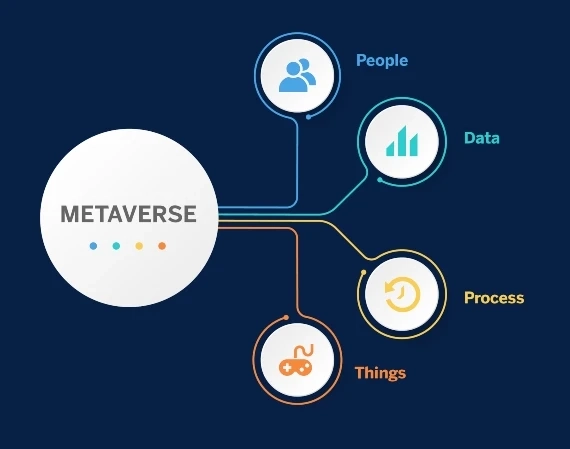
The Pillars of the Metaverse
People : Connect people in a more valuable wayData: Turn data into intelligence to make better decisionsProcess: Sending the right information to the right person (or machine) at the right timeThings: Physical and virtual devices and objects connected to the Internet and to each other to make intelligent decisionsMetaverse Challenges
No new blockchain technology or concept can emerge without challenges, and the metaverse is no exception:
Identity management: In today's Web 2.0 applications, it is difficult to confirm the identity of the user. With the metaverse, the problem is even greater, because the use of products and services is expanded. You wouldn't want the metaverse to be a "wild West."Data Security and Privacy (SSP): As devices and people become more connected and collect more data, the expansion of the metaverse will accelerate to a rate close to that of the real universe. Therefore, the unknowns about privacy, security and protection will also increase. Critical to the future of the metaverse will be how companies find the right balance between the rich data in this environment and customer privacy. More importantly, it will be decisive for the customer's confidence in the metaverse or any other form of fictional universe.Financial services in the metaverse: The use of a Cryptocurrency is already a challenge in itself. Using it as a payment method in the metaverse will add even more complications to what is not yet a regulated payment system. One solution could be a CBDC (digital currency issued by a central bank).Regulations and means of protection: The metaverse is an unknown territory that the law must explore to define the responsible actors and create regulations that protect users. Intellectual property, such as the new NFTs (digital assets in the form of “non-fungible tokens”), will also need to be safeguarded.The emotional and mental impact of living in the metaverse: The problems that arise from the non-stop use of social networks and online video games will be transferred to the metaverse, but on a larger scale, since another dimension is added - real-time interactions - that could create psychological disorders in the real world. The border that separates the real world from the imaginary will blur.Metaverse standardization: This is often one of the most problematic factors in the early life cycle of a new technology, as everyone wants to set themselves as the “standard” and dominate the market. Norms and standards cover all hardware and software, processes and protocols, and interoperability will be critical to the design and development of the metaverse.What Does the Future Hold?
Data is embedded in everything we do. Each blockchain development company needs its own data strategy, which requires comprehensive leadership in this area. The metaverse will give rise to tens of millions of new objects and sensors, all generating data in real time. This will add value to the products and services of companies that use the metaverse as a new business channel. The technology of the metaverse will offer companies enormous possibilities. There will be a virtually inexhaustible list of products and services that will be sold in various markets, both vertical and horizontal.
To give a few examples: In e-commerce, instead of the current two-dimensional click-to-buy model, a new revenue stream will be created in the metaverse from digital products purchased synchronously. In sales and marketing, it will be common to connect with the customer and exchange experiences about the product or service virtually. This may be reminiscent of the virtual meetings of the past two years during the pandemic, but in the metaverse it will be a much more "real" and productive experience. Cryptographic products, such as NFTs, will be native objects of the metaverse, constituting another piece of the Web 3.0 puzzle.
Lastly, similar to the cloud, there will be private, hybrid, and public metaverses, with all possible applications and services in each. Businesses will benefit from all options depending on their capabilities and needs. The main objective is to achieve the "metaverse as a service" (MaaS) and the corresponding certification and labeling for products and services.