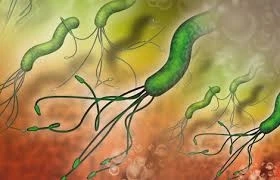
Helicobacterpylori (HP) is a Gram-negative bacterium, which causes chronicinfection and inflammation of the duodenum and stomach resulting inulceration. H. pylori reside in 80-90% of affected patients withulcerative gastroplication and in 90% of affected patients withduodenal ulcerative colitis. These bacteria are frequently associatedwith the leaky gut syndrome. Helicobacter pylori produce significantamounts of antigens that trigger an immune response and promote thegrowth of malignant epithelioid monoclonal cells (MMPs), which areidentified as the cause of inflammatory bowel disease. Helicobacterpylori have also been implicated in the pathogenesis of Crohn'sdisease and in the occurrence of allergic ulcers in human milk.
Thewidest HelicobacterPylori Diagnosticsare the clinical serological tests. The most important parameter toconsider is the identification of antibodies to the transgenicfactor, sphingosine, which is located on the helical tail of thebacterium. It has been postulated that humans have a natural geneticimmunity to Helicobacter pylori but this has not been fully tested.The clinical serological tests are designed to detect the presence ofantibodies to the transgenic factor and any related antibodies,whether known or not, that might be related to other conditions andinfections such as HIV and hepatitis.
SeeFull Report@ https://bit.ly/3AwxT1N
ReadMore@ https://bit.ly/3wheaQC