Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG regulations) have become a crucial aspect of corporate responsibility, ensuring that businesses operate sustainably and ethically. These regulations establish standards for companies to follow, promoting environmental protection, social responsibility, and transparent governance. With governments and investors prioritizing sustainability, businesses must adapt to meet compliance requirements and maintain a competitive edge.
The Importance of ESG Regulations
These regulations are designed to address key challenges in sustainability and corporate ethics. They encourage organizations to adopt practices that reduce environmental impact, support social well-being, and uphold strong governance policies. These regulations benefit not only businesses but also investors, consumers, and communities by ensuring long-term stability and ethical operations.
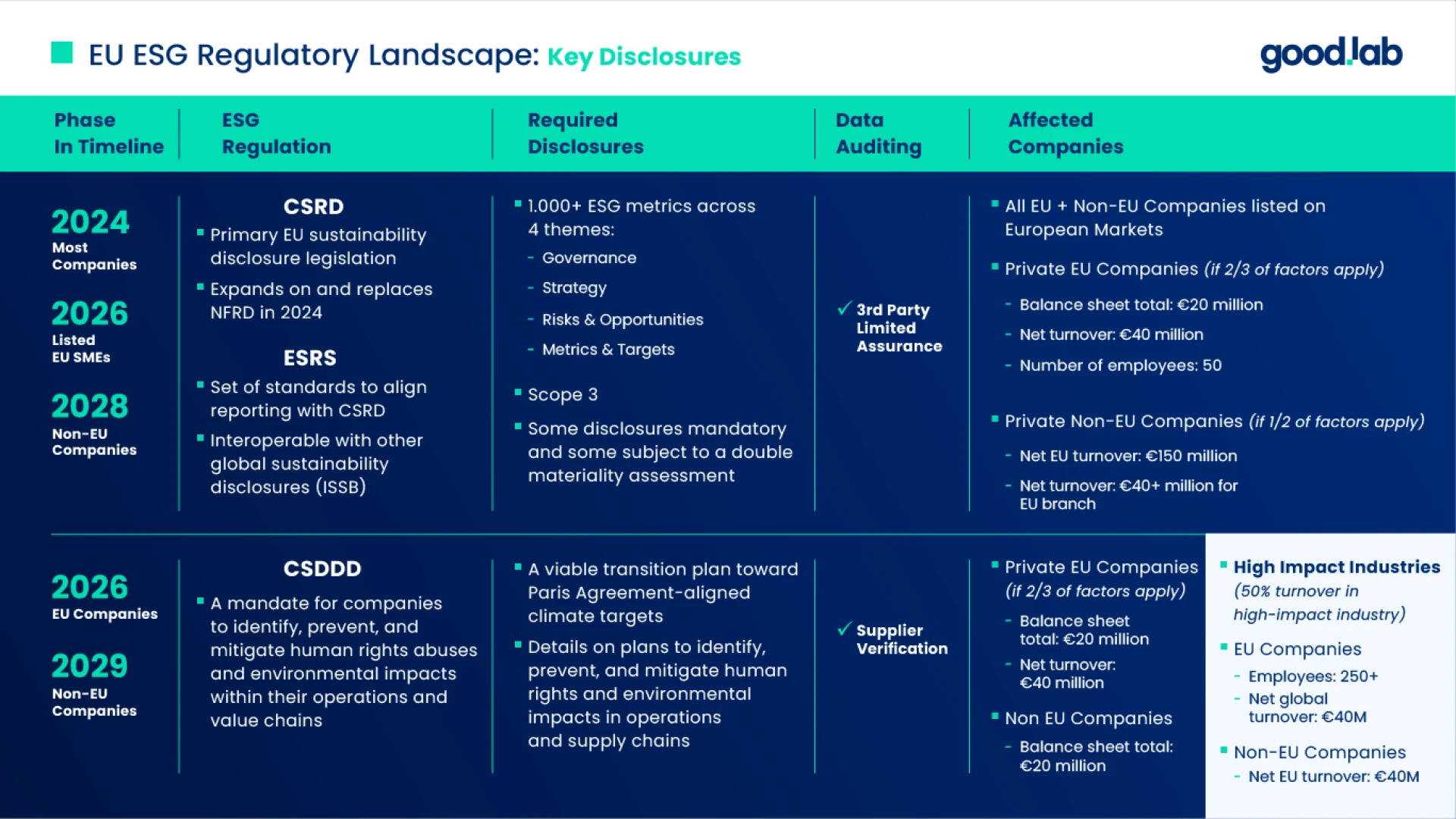
Key Components of ESG Regulations
1. Environmental Compliance
Companies must comply with environmental standards that focus on reducing carbon footprints, managing waste, and promoting energy efficiency. Some major aspects of environmental regulations include:
- Carbon Emissions Reporting: Businesses must track and disclose greenhouse gas emissions, including Scope 1, 2, and 3 emissions.
- Sustainable Resource Use: Regulations encourage the use of renewable energy and responsible sourcing of raw materials.
- Pollution Control: Industries must follow guidelines to minimize air, water, and soil pollution.
2. Social Responsibility
Social aspects of ESG compliance focus on workplace ethics, labor rights, and community engagement. Companies are required to:
- Ensure Fair Labor Practices: Regulations prevent discrimination, child labor, and workplace exploitation.
- Promote Diversity and Inclusion: Businesses must implement policies that support equal opportunities and fair wages.
- Maintain Consumer Protection Standards: Companies must ensure product safety, ethical advertising, and data privacy.
3. Governance and Transparency
Governance regulations establish ethical corporate policies, emphasizing accountability and transparency. Key areas include:
- Corporate Reporting: Companies must disclose financial and sustainability performance metrics.
- Board Diversity and Ethics: Regulations promote independent boards and gender diversity in leadership roles.
- Anti-Corruption Policies: Businesses must follow anti-bribery laws and prevent financial fraud.
Global ESG Regulations and Their Impact
European Union (EU) ESG Framework
The EU has implemented strict ESG regulations to enhance corporate sustainability. Some key directives include:
- Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD): Requires large and listed companies to disclose sustainability performance.
- European Sustainability Reporting Standards (ESRS): Establishes guidelines for ESG reporting.
- Corporate Sustainability Due Diligence Directive (CSDDD): Ensures businesses identify and mitigate environmental and human rights risks.
United States ESG Policies
While the U.S. does not have a unified ESG framework, regulations such as the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) disclosure requirements and the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) policies influence corporate sustainability reporting.
Asia-Pacific ESG Standards
Countries like Japan, China, and Australia have introduced regulations focusing on climate risk reporting, corporate social responsibility (CSR), and governance ethics.
Challenges in ESG Compliance
Companies face several challenges when implementing these regulations, including:
- Data Collection and Reporting: Tracking ESG metrics can be complex and resource intensive.
- Regulatory Differences Across Regions: Compliance requirements vary between countries, making it difficult for multinational companies to standardize practices.
- Financial Costs: Transitioning to sustainable operations requires significant investment in technology, training, and compliance systems.
Future of ESG Regulations
With an increasing global focus on sustainability, ESG regulations will continue to evolve. Businesses must stay informed about policy changes and adopt proactive strategies to align with emerging standards. By integrating ESG principles into their core operations, companies can enhance their reputation, attract investors, and contribute to a more sustainable future.


