Introduction
In a world where our resources are finite, the need for sustainable practices has never been more apparent. The traditional linear economic model, characterized by a "take-make-waste" approach, has led to environmental degradation, resource depletion, and economic inefficiency. Enter the circular economy—a groundbreaking concept that offers hope for a more sustainable future. In this blog, we'll explore the fundamentals of circular economy solutions, their benefits, and some innovative solutions paving the way for a brighter and greener tomorrow.
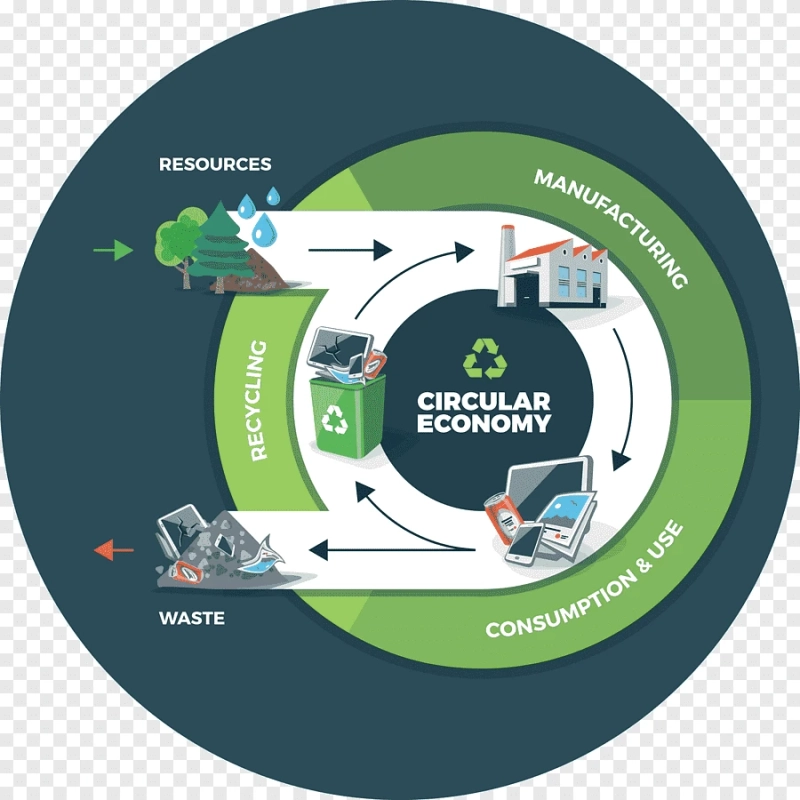
What is the Circular Economy?
The circular economy is a holistic and regenerative approach to economic activity that aims to minimize waste and make the most of resources. Unlike the linear economy, where products are manufactured, used, and then discarded, the circular economy envisions a continuous cycle of product use, recovery, and regeneration. It revolves around three key principles:
1. Design for Longevity and Reuse
In a circular economy, products are designed with durability and reuse in mind. This means creating items that can withstand wear and tear, are easily repairable, and can be disassembled for component replacement.
2. Resource Efficiency
Efficiency is the name of the game in the circular economy. Resources are conserved and used as efficiently as possible, reducing waste generation and minimizing environmental impact.
3. Regenerative Practices
The circular economy seeks to restore and replenish natural systems. It promotes practices like recycling, upcycling, and reusing materials to minimize the extraction of new resources and reduce pollution.
Now that we've grasped the basics, let's dive deeper into the advantages of embracing the circular economy.
The Benefits of Circular Economy
Environmental Benefits
1. Reduced Resource Depletion
One of the primary benefits of the circular economy is the preservation of natural resources. By extending the life of products and materials, we reduce the demand for raw materials, protecting our ecosystems.
2. Lower Greenhouse Gas Emissions
The circular economy model aims to minimize waste generation and the associated emissions from landfills and incineration. It also promotes cleaner production processes, further reducing carbon footprints.
3. Biodiversity Conservation
With a reduced need for resource extraction and a focus on regenerative practices, the circular economy helps safeguard biodiversity and natural habitats.
Economic Advantages
1. Cost Savings
Embracing circularity can lead to significant cost savings for businesses. By reusing materials and extending product lifecycles, companies can reduce procurement and disposal costs.
2. Job Creation
The circular economy fosters new job opportunities in recycling, remanufacturing, and repair industries. These jobs often have a positive impact on local communities.
3. Enhanced Resilience
A circular economy is less vulnerable to supply chain disruptions and resource scarcity, enhancing economic resilience in the face of global challenges.
Social Benefits
1. Access Over Ownership
Circular business models, such as sharing and leasing, offer consumers access to products rather than ownership. This can lead to reduced consumerism and a more sustainable lifestyle.
2. Community Engagement
Circular initiatives often involve communities in repair and recycling activities, fostering a sense of empowerment and collective responsibility for environmental stewardship.
3. Innovation and Creativity
The circular economy encourages innovative solutions for product design, recycling processes, and sustainable business models, driving technological advancements.
Circular Economy Solutions in Action
1. Product-as-a-Service (PaaS)
What is PaaS?
Product-as-a-Service is a business model where customers pay for the use of a product rather than owning it. Companies retain ownership of the product and are responsible for maintenance, repair, and eventual recycling.
How does it work?
Imagine subscribing to a laptop service rather than buying one. You get the latest model, regular updates, and repairs included in your subscription fee. When the laptop reaches the end of its life, the company takes it back for recycling.
2. Upcycling and Repurposing
What is Upcycling?
Upcycling is the process of transforming waste materials or unwanted products into new, higher-value items. It's a creative way to breathe new life into discarded materials.
How does it work?
Old jeans can be upcycled into fashionable bags, glass bottles can become stylish lamps, and shipping containers can be turned into modular housing. Upcycling not only reduces waste but also adds artistic flair to the products.
3. Closed-Loop Supply Chains
What are Closed-Loop Supply Chains?
Closed-loop supply chains involve collecting and reusing or recycling products and materials at the end of their life cycles. This approach minimizes waste and maximizes resource efficiency.
How do they work?
Companies like Patagonia have implemented closed-loop supply chains for their clothing. Customers can return worn-out clothing for recycling, with the material being used to create new products.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1: How can individuals contribute to the circular economy?
A: Individuals can contribute by embracing the "reduce, reuse, recycle" mantra, supporting sustainable businesses, and participating in community repair and swap events. Additionally, making conscious purchasing decisions and opting for longer-lasting products can make a significant difference.
2: Is the circular economy only relevant to manufacturing?
A: No, the circular economy concept is applicable across various industries, including agriculture, fashion, and technology. It can be implemented at multiple stages of a product's lifecycle, from design and production to consumption and disposal.
3: Are there any challenges to implementing a circular economy?
A: Yes, challenges include shifting consumer behavior, overcoming regulatory barriers, and transitioning from traditional linear business models. However, these challenges can be addressed through innovation, collaboration, and public awareness.