Anthrax Disease Overview:
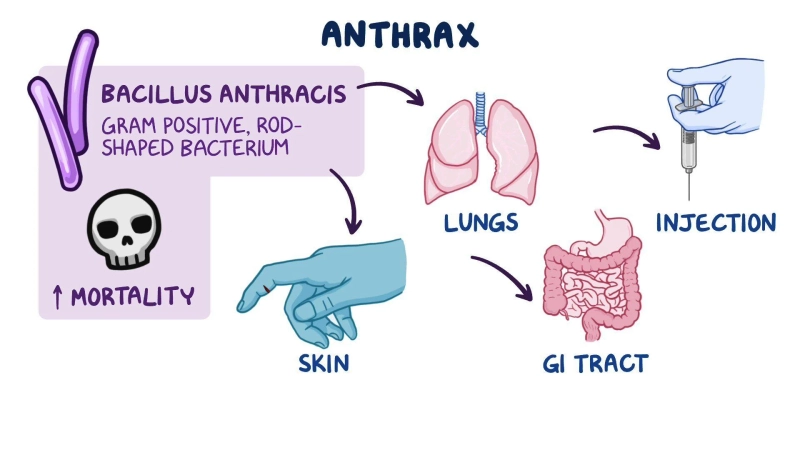
Anthrax Disease is a potentially lethal infectious disease caused by the bacterium Bacillus anthracis. This pathogen can infect both humans and animals, making it a zoonotic disease. It primarily affects herbivores, but humans can contract it through direct or indirect contact with infected animals or their products. Understanding the diagnostic methods, treatment options, and regulatory framework surrounding anthrax is crucial for effective prevention and management.
There is anthrax everywhere on Earth. It primarily affects animals in agricultural settings, where it is common. It is more common in developing countries or those without veterinary public health policies. There are more cases of anthrax reported in some regions of the world than others.
The Market Competitors Listed Below are Revolutionizing Healthcare with Innovative Diagnostic Inventions:
Becton, Dickinson, and CompanyInnovia MedicalWorld Precision InstrumentsIntegra LifeSciencesCipla LimitedSun Pharmaceuticals Industries LtdFortis HealthcareIdaho Technology, Inc.OthersThe Market Competitors Listed Below are Revolutionizing Healthcare with Innovative Diagnostic Inventions:
Cipla Ltd.Ralingtonpharma LLPEmergent BioDefense Operations Lansing LLCElusys Therapeutics, Inc.Sfl Pharmaceuticals Deutschland Gmb HEmergent Manufacturing Operations Baltimore LLC.Reddy's LaboratoriesEmergent Product Development Gaithersburg Inc.Cangene CorporationOthersDiagnostic Analysis:
Clinical Symptoms:
Anthrax can present in different forms: cutaneous, inhalation, and gastrointestinal. Cutaneous anthrax, the most common form, manifests as skin lesions with a central ulcer and surrounding edema. Inhalation anthrax, the most severe form, resembles flu-like symptoms initially but progresses rapidly to severe respiratory distress. Gastrointestinal anthrax results from ingesting contaminated meat and presents with severe abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea.
Laboratory Tests:
Gram Staining: Identifies the presence of gram-positive spore-forming rods, characteristic of Bacillus anthracis.Culture: Isolates the bacteria from clinical samples, aiding in definitive diagnosis.PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction): Amplifies specific DNA sequences of the bacteria, offering a rapid and sensitive diagnostic tool.Serological Tests:
ELISA (Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay): Detects antibodies against Bacillus anthracis in the patient's serum.Immunofluorescence Assay (IFA): Identifies specific antigens in clinical samples.Treatment Analysis:
Antibiotics:
Prompt administration of appropriate antibiotics is vital for successful treatment. Ciprofloxacin, doxycycline, and penicillin are commonly used.
Supportive Care:
Depending on the form and severity of the disease, patients may require respiratory support, intravenous fluids, and wound care.
Vaccination:
Anthrax vaccine is available for individuals at high risk of exposure, such as military personnel and laboratory workers.
Regulatory Framework:
CDC (Centers for Disease Control and Prevention)
The CDC provides guidelines for the diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of anthrax. They also oversee the management of potential anthrax outbreaks.
WHO (World Health Organization):
The WHO offers global policies and strategies for anthrax prevention and control, working in collaboration with member countries.
Browse More Information:
https://www.diseaselandscape.com/infectious/anthrax-disease-market-penetration-strategy
Clinical Assessment:
Prognosis:
Early diagnosis and treatment significantly improve prognosis. Inhalation anthrax has the highest mortality rate, even with aggressive treatment.
Long-term Effects:
Survivors of severe cases, especially inhalation anthrax, may experience lingering respiratory issues and psychological trauma.
Market Trends Analysis:
Pharmaceuticals:
The market for anthrax-related pharmaceuticals, including antibiotics and vaccines, has seen steady growth due to ongoing research and development efforts.
Biodefense:
Governments and organizations invest in research and stockpiling of anthrax-related countermeasures as part of biodefense strategies.
Regional Insights:
High-Risk Regions:
Certain areas, particularly those with agricultural economies or regions prone to bioterrorism threats, may have higher incidences of anthrax.
Preventive Measures:
Regions with a history of anthrax outbreaks implement strict protocols for livestock vaccination and handling.
Conclusion:
Understanding the diagnostic methods, treatment options, and regulatory framework surrounding anthrax is crucial for both healthcare professionals and policymakers. Timely intervention, along with preventive measures, plays a pivotal role in minimizing the impact of this potentially deadly disease.
Browse Through More Infectious Diseases Research Reports.
Related Reports:
Insights and Trends in the Global Landscape of Lung Cancer Services
The symptoms, transmission, and precautions of Monkeypox
The Myths of Pneumonia: Symptoms, Causes, and Prevention Methods
Navigating the Complex Autoimmune Disorder of Lupus
Ringworm Comprehensive Guide: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment