Email authentication is vital to successful webmail administration. It provides a way for users to verify that the email they receive really is from the organization it claims to be from. DKIM (Domain Keys Identified Mail) is a public-key cryptography method that forces email servers to use public-keys instead of domain names when authenticating email accounts. This improves security and privacy for users in two ways: it prevents spoofing and man-in-the-middle attacks, and it improves the usability of email services since all emails are authorized by their original originator.
DKIM is often thought of as email encryption, but it’s more than that. With DKIM, your email provider can be held responsible for any email you send that falls into the wrong category, even if it looks like it came from your intended recipient. This can help you protect yourself against spammers and prevents them from sending you marketing emails that are designed to look like they come from genuine sources. Email is still the most popular way for communication in the modern digital world. But the quality of email can be less than stellar: 23% of businesses say their customers receive less important information than other channels, and 28% receive spam emails. How could this be? Almost half of all emails are addressed to someone who isn’t actually interested in the topic being discussed. This is what makes data-analytics tools valuable: they can help identify these potential spammers.
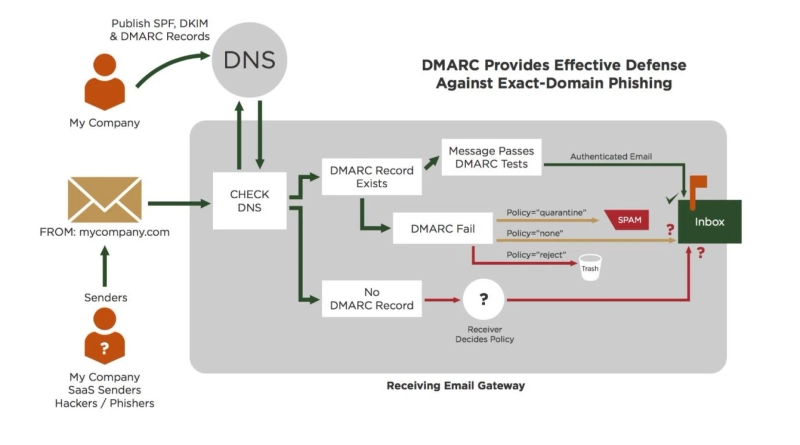
The DomainKeys International (DK IM) service allows you to protect your domain from being flagged for spam or other unwanted interference. It generates a unique digital address for every email from your domain name and other third-party domain records. This helps to make sure that recipients see your email from the source. It also works with third-party email delivery services and integrates with numerous other spam blocking features in browsers and apps that support domain filtering technology. Email has become one of the most important tools in employees’ hands. Companies are faced with many attacks including phishing scams that attempt to steal employee data. Employees need to feel safe sending their work-related emails and receiving important updates from clients, partners and other company representatives. The good news is that there are simple yet effective ways to validate emails and reduce fraud attacks: DKIM, SPF, and DMARC. The bad news is that not many organizations include these in their email security strategy.
What is DKIM and how does it work?
DomainKeys identified mail systems work by comparing data in both the sender's and recipients public keys. If they match, the message has been received correctly by both systems—and no duplicate messages have been sent between the two parties. DKIM is useful for both sender and recipient-importers because it provides an additional level of encryption when sending emails, protecting the data transferred during transmission as well as improving email delivery reliability. The idea behind DKIM is to make it easy for people to verify that the addresses they receive emails from are genuine. The email server can display a SHA-256 digest of the message as well as the domain key within the HTML body of an email.
This information is sufficient for DKIM to verify an email's authenticity with other email services. Domains delegated keys include keys used for encryption and digital signing. They are used by online services to authenticate and encrypt messages for end-to-end encrypted sessions. They can also be used with servers that implement also secure authentication procedures, such as a username and password combination. The DKIM solution provides an infrastructure for key exchange which improves upon the commonly used public-key infrastructure (PKI) protocol. DKIM uses public-key cryptography to authenticate messages from senders' domainkeys to recipients' domainkeys.
The protocol works on the principle of zero knowledge: if you have no knowledge of the other party's public key, then you can't verify a message's content against the public key in your database. The idea is to make it difficult for spammers to send mass emails with forged signatures, or to create email accounts under someone else’s name. The main problem with old email encryption was that there wasn’t much in the way of a standard way for signing emails, meaning it was easy for spammers to create addresses that looked real and created email addresses that looked like they came from the real domain owners.
The DKIM signature
The Domain Name Identification (DNS) protocol and its associated Message Authentication Scheme (MCS) are mandatory for sending e-mail. The DKIM signature verifies that both the message and the who is information belong to the person or organization sending the message. The main purpose of DNS is to prevent spoofing, i.e. sending the same e-mail to multiple recipients. Spoofing can result in the loss of reputation or even damage to a business reputation. This makes it possible for almost anyone to add an email signature that reflects their own personal style. The choice of what to add in the header is not something that should be taken lightly. It has profound consequences for how your message will be received by your recipients and the domains they receive emails from.
That is why it is critical that you get this right: make sure you choose a domain name that reflects who you are, not what others think you should be. To validate a domain, a mail transfer agent generates a random 128-bit key, called a DKIM signature. This key protects the domain against modification by sending it to several different places in the Internet simultaneously. The DKIM signature is combined with a 128-bit public key, known by the domain owner to be connected to the originating address. The combined signature checksum allows mails to be checked for authenticity.
Importance of DKIM
In simple words, DKIM is a digital signature which can be used to verify the identity of a sender. For emails, it proves the email came from the intended recipient’s address and can be used to verify receipt of an email or resolve disputes about whether an email has been received by the recipient. The use of DKIM is recommended for all mails because it helps improve email security, decreases spammer levels and can speed up delivery time. The fundamentals of digital identity are being set out for all to see and it's time we took responsibility for our digital footprint. We have the freedom of speech and expression online but must realise that mistakes we make in transferring data means that our identities might be vulnerable.
How Emailauth can help
DKIM is a good first step in email authentication, and it can be done using Emailauth.One of the hundreds of checks Emailauth makes against incoming emails includes validating DKIM, SPF and DMARC records.
source by:-https://atozcybersecurity.blogspot.com/2021/08/what-is-dkim-and-why-you-need-it.html