The peritoneum is an abdominal membrane cavity that covers the abdominal wall and organs.
Peritoneal Dialysis is carried out using a thin, soft and permanently inserted tube (catheter) comprised of silicone. It is implanted through the abdomen cavity using minimal surgery.
Peritoneal Dialysis is performed in two methods:
1- CAPD (Continuous Ambulatory Peritoneal Dialysis):
Under the patient's body's structure, 100 to 1000 mL of the dialysis solution for infants and 2000- 2500 mL for adults are administered to the abdomen. Following the treatment, the body is within the stomach cavity for around 4-6 hours before being replaced by a different solution. This is when the waste products like creatinine and urea in blood and the excess fluids in the body are absorbed through the dialysis fluid. The delivery and release of dialysis fluid to the abdominal cavity is done through gravity. Dr. Q Khan provides the best Coordinator Transplant Coordinator in the USA. This procedure is known as the "Dialysis Bag Replacement Process". Dialysis is done by the patient at least 4-5 every day. Peritoneal Dialysis performed by this method is known as CAPD (Continuous Ambulatory Peritoneal Dialysis).
2. APD (Instrumental Peritoneal Dialysis)
Peritoneal Dialysis at home with an apparatus is APD (Instrumental Peritoneal Dialysis). For this type of therapy, the person puts the solution bag, sets it in the peritoneal dialysis device before going to bed, and program the machine as advised. In the evening (8-10 hours), when the patient is sleeping, the device pumps dialysis fluid into the abdomen cavity. It then keeps the fluid in reserve and eventually empty. The treatment can be modified depending on the health of the patient.
GOOD ASPECTS OF PERIODIC DIALYSIS
After having been trained through the peritoneal dialysis nurses, the patient can perform the treatment on his own so that his dependence on the hospital decreases
. The intake of fluids and food is more tolerant.
Controlling blood pressure could be better provided.
There isn't any bleeding as with hemolysis.
The training is simple, and its time is minimal.
It is a highly sought-after treatment method, particularly for children and elderly patients, because the strain to the cardiovascular system remains less.
The tip on the end of the tube, which is to be inserted into the peritoneal cavity, are small holes that will allow for the flow and exit of dialysis fluid. There are two felt bands around the catheters. The felts are knitted by the body's connective tissue and stop the catheter from slipping off. Connective tissue also blocks microbes from entering your organ through the catheter.
Titanium Adapter:
It's a piece of titanium made of metal located between it and the transfer device. It serves as the bridge between the transfer set and the catheter. It is a permanent part and cannot be replaced.
Transfer set:
This set serves as an intermediary set that allows an interface with a Titanium adapter. It is recommended to change it every about 4-6 months. In addition, when the edge of the set is damaged or opened in any manner, it should be replaced immediately, without Dialysis. The transfer set should be changed at the hospital and then with the help of the nurse who is in Dialysis.
Mini Ax:
It is a white-coloured cap with an antiseptic-impregnated sponge attached to the end of the transfer set after the dialysis process is completed. The lid is clean, and the inside is not to be handled. The mini valve stops bacteria from entering inside the stomach cavity. The expiry date printed on the mini cap should be verified. If it's past its expiry date, it shouldn't be used.
An entirely new cap must be used with every dialysis process.
Dialysis Solutions:
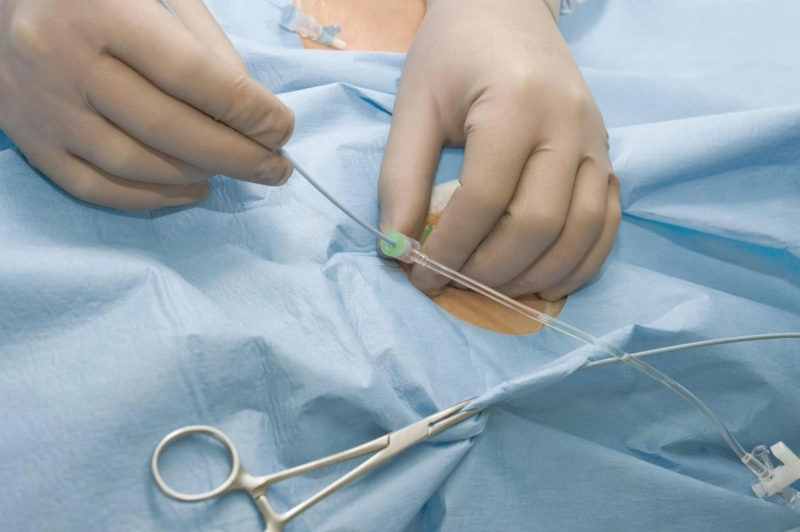
The catheter is inserted within the functional area or the dialysis centre.
The dialysis centre determines which method is used depending on the patient's condition. Once the catheter has been inserted into the abdomen, a control film will be required to locate the catheter site within the abdomen. When the catheter is in, the dressing shouldn't be removed for a period of four to seven days to allow healing to occur (if there isn't any bleeding, wetness, etc.). The procedure should be carried out through the nurse in Dialysis. In general, Dialysis begins three months after the catheter has been placed. The patient's education has been completed. The time for starting Dialysis could be reduced or prolonged if needed.
CATHETER EXIT LOCATION
The catheter exits from the body is referred to as the exit point of the catheter. The portion of the catheter which runs beneath the skin is known as the tunnel.
Once the catheter is in at the exit site, the dressing must be checked frequently.
* The daily care of the site where you exit your medical centre recommends your catheter.
Redness and swelling, pain and leakage of fluid that indicate an infection in the dressing are not to be ignored.
These signs suggest that there are microbes near the catheter's exit site. If any of these symptoms occur, the dialysis centre must be called. Suppose it's too late to resolve these issues. Dr. Q Khan provides the best Transplant dietitian consultant in the USA. In that case, the microbes can enter the tunnel via the catheter exit point and eventually enter the tunnel that could trigger it to cause the catheter to get taken out.
CATHETER EXIT SITE CARE
For a successful catheter exit location, the movement of the portion of the catheter that is outside the body is to be avoided.
The skin around the site of the catheter exit, and the subcutaneous portion covers the catheter, which ensures the integration of the catheter into the skin. If the movement of the catheter isn't stopped, the integration process will not be attained, and a space is created in which microbes could quickly colonize in the skin and trigger inflammation.
THINGS TO PAY ATTENTION
Masks must be worn while dressing.
Hands must be washed thoroughly before making contact with the catheter.
The catheter should not be pulled or twisted.
Needles and scissors should not be used close to the catheter.
0