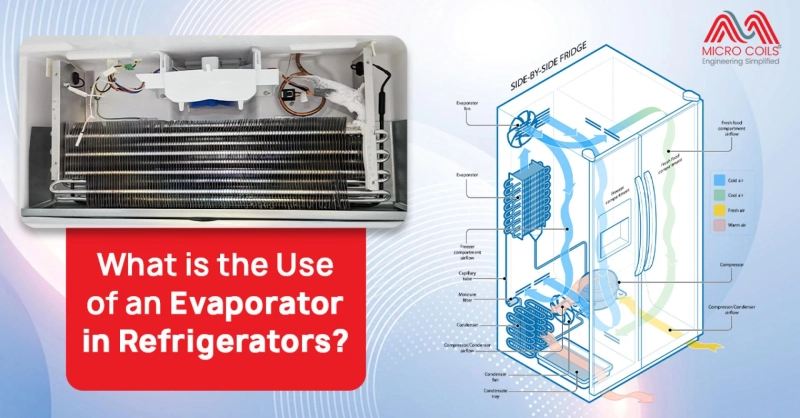
The evaporator is a crucial component in a refrigerator’s cooling system. It plays a vital role in absorbing heat from the stored food and keeping the internal temperature low. Without an evaporator, a refrigerator would not function efficiently. This guide explains the purpose of an evaporator in a referigeration system: how an evaporator works, its types, applications, advantages, and maintenance tips.
What is an Evaporator?
An evaporator is a heat exchanger that absorbs heat from inside the refrigerator and transfers it to the refrigerant. The refrigerant inside the evaporator changes from liquid to gas, which helps lower the temperature inside the appliance.
How Does an Evaporator Work?
- Heat Absorption – The evaporator is located inside the refrigerator compartment, where it absorbs heat from stored items. As warm air circulates inside the fridge, it comes into contact with the evaporator coils, which are much colder due to the refrigerant inside. The heat from the air is absorbed by the coils, cooling the air inside the fridge.
- Refrigerant Flow – The refrigerant inside the evaporator starts as a low-pressure liquid. As it absorbs heat from the refrigerator compartment, it turns into a gas through the process of evaporation. This phase change allows it to efficiently carry heat away from the stored food.
- Temperature Regulation – The cooled air inside the refrigerator condenser coil is maintained at a constant temperature by the thermostat. The cycle repeats as the refrigerant flows back to the compressor, where it is pressurized and cooled again before returning to the evaporator.
Types of Evaporators in Refrigerators
- Plate Evaporator – A thin metal plate contains the refrigerant. It is commonly used in direct cool refrigerators, where cooling is achieved through natural convection rather than forced air circulation. This type is energy efficient but may result in uneven cooling.
- Finned Evaporator – Metal fins increase the surface area for better heat absorption and efficient cooling. This design improves heat exchange between the refrigerant and the surrounding air, allowing for faster and more uniform cooling.
- Tube and Wire Evaporator – A simple design where a coiled tube runs through the refrigerator, cooling it effectively. This type is often found in older refrigeration systems and requires more space but provides reliable performance.
- Forced Convection Evaporator – Uses fans to circulate air over the evaporator coils, ensuring uniform cooling. This type is commonly used in modern frost-free refrigerators, preventing ice buildup and maintaining consistent temperatures.
- Flooded Evaporator – Used in larger refrigeration systems where excess refrigerant ensures better heat transfer. This design allows the refrigerator evaporator to handle high cooling loads and is often found in industrial refrigeration systems.
Applications of Evaporators in Refrigerators
- Household Refrigerators – Maintains freshness of food by keeping the temperature low. The evaporator ensures that perishable items like dairy, vegetables, and meat remain safe for consumption.
- Commercial Refrigeration – Used in restaurants, grocery stores, and cold storage facilities. These systems require powerful evaporators to manage large quantities of stored goods.
- Industrial Cooling Systems – Essential for food processing and pharmaceutical storage. Evaporators in these systems help maintain stringent temperature requirements for sensitive products.
- Medical Refrigeration – Keeps vaccines and medicines at controlled temperatures. Pharmaceutical refrigerators use precise evaporator systems to prevent temperature fluctuations that could spoil medical products.
- Beverage Cooling – Used in vending machines and coolers to keep drinks chilled. These systems rely on efficient evaporators to maintain a steady, cool temperature for beverages.
Advantages of an Efficient Evaporator
- Faster Cooling – Quick heat absorption ensures rapid temperature reduction. This helps keep food fresh for longer periods.
- Energy Efficiency – Reduces power consumption by optimizing heat transfer. A well-designed evaporator minimizes the workload on the compressor, leading to lower electricity bills.
- Even Temperature Distribution – Prevents hotspots and maintains consistent cooling. This is particularly important for commercial refrigeration systems storing sensitive items.
- Improved Food Preservation – An evaporator in a refrigeration system reduces spoilage by maintaining low temperatures. A well-functioning evaporator extends the shelf life of perishable goods.
- Longer Refrigerant Life – Properly functioning evaporators extend refrigerant efficiency. Efficient heat exchange means the refrigerant doesn’t need to be replaced as often.
Installation Tips
- Correct Placement – Ensure the evaporator is positioned properly for optimal airflow. A poorly placed evaporator can result in uneven cooling and inefficiency.
- Secure Connections – Avoid leaks by properly sealing refrigerant lines. Even a small leak can reduce cooling performance and increase energy consumption.
- Proper Insulation – Helps maintain efficiency by reducing heat exchange losses. Insulated evaporators minimize temperature fluctuations and improve energy savings.
- Adequate Ventilation – Prevents overheating and improves performance. Good airflow around the evaporator allows for efficient heat exchange and consistent cooling.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting
- Regular Cleaning – Dirt and debris buildup reduce efficiency, so clean it periodically. A dirty evaporator restricts airflow, making the refrigerator work harder.
- Check for Frost Buildup – Excess frost can block airflow and affect cooling. Defrost the evaporator when necessary to prevent inefficiencies.
- Inspect for Leaks – Refrigerant leaks can lead to inefficient cooling and increased energy costs. Look for signs of oil stains or refrigerant loss.
- Monitor Temperature – Inconsistent cooling may indicate evaporator issues. If your refrigerator isn't staying cold, the evaporator might not be functioning properly.
- Ensure Proper Air Circulation – Blocked vents reduce efficiency and create uneven cooling. Keep storage areas clear to allow air to circulate freely.
Common Issues and Solutions
- Excessive Frost Formation? This could be due to a faulty defrost system or poor airflow. Regularly check and defrost to prevent ice buildup.
- Refrigerator Not Cooling? Check for refrigerant leaks, clogged coils, or a malfunctioning evaporator fan. If the evaporator isn’t cold, there may be an issue with the refrigerant cycle.
- Unusual Noises? Loose components or ice buildup can cause operational noises. Inspect the evaporator fan and coils for obstructions.
- Water Leakage? A blocked drain tube or defrost malfunction could be the culprit. Ensure proper drainage to prevent pooling water inside the fridge.
- High Energy Consumption? A dirty or damaged refrigeration coil reduces efficiency, leading to higher power usage. Routine maintenance can help keep energy costs low.
Safety Precautions
- Turn Off Power Before Maintenance – Prevents electrical hazards when cleaning or inspecting.
- Use Proper Tools – Avoid damage to delicate evaporator components by using the right equipment.
- Handle Refrigerant Carefully – Exposure to refrigerant gases can be harmful, so work in a well-ventilated area.
- Wear Protective Gear – Safety glasses and gloves prevent accidental injuries during maintenance.
Choosing the Right Evaporator for a Refrigerator
- Consider Cooling Needs – Different types suit different applications, from household to industrial use.
- Evaluate Material Durability – Stainless steel or aluminum evaporators last longer and resist corrosion.
- Assess Energy Efficiency – A high-efficiency evaporator reduces power consumption.
- Check Compatibility – Ensure the evaporator matches the refrigerator’s system design.
- Look for Advanced Features – Some modern evaporators have self-cleaning mechanisms and improved heat transfer capabilities.
Conclusion
The evaporator is an essential part of a refrigerator’s cooling system. It plays a significant role in maintaining the desired temperature, preserving food, and improving energy efficiency. Proper installation, maintenance, and troubleshooting help maximize its lifespan and performance. Understanding the different types, the function of evaporator in refrigerators, and advancements in evaporator technology allows consumers to make informed choices when selecting refrigeration systems. With ongoing innovations, evaporators continue to become more efficient, sustainable, and effective in cooling applications.