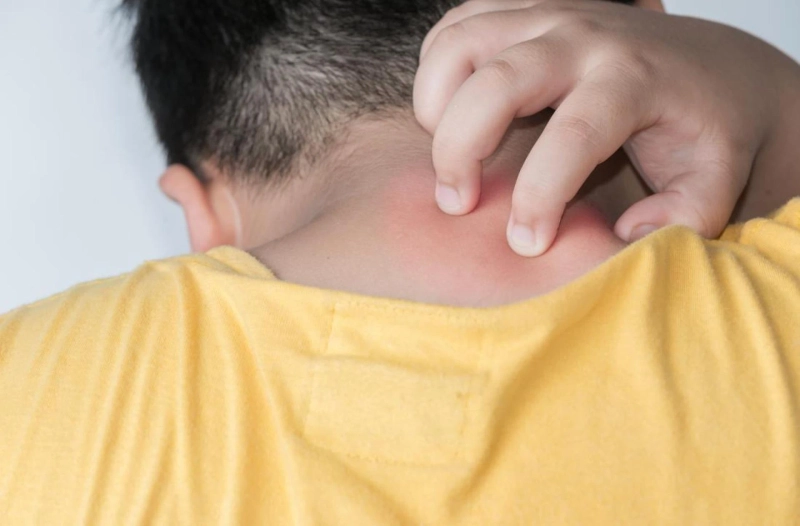
Spongiotic dermatitis, commonly known as eczema, is a skin condition characterized by itchy, inflamed, and often red patches of skin. It can affect individuals of all ages and varies in severity. Understanding when to seek medical advice for spongiotic dermatitis is crucial in managing the condition effectively and preventing complications.
This blog will explore the signs, symptoms, and when to see a doctor for spongiotic dermatitis, ensuring optimal care and relief.
An Overview of Spongiotic Dermatitis
Spongiotic dermatitis occurs due to inflammation in the epidermis, leading to fluid accumulation between skin cells. This condition manifests in various forms, including atopic dermatitis, contact dermatitis, and seborrheic dermatitis. Each type has distinct triggers and patterns, yet they share common symptoms such as redness, itching, and swelling.
Prevalence of Spongiotic Dermatitis
Spongiotic dermatitis, a common inflammatory skin condition, effects approximately 10-20% of children and 1-3% of adults worldwide, with atopic dermatitis being the most prevalent form. Studies indicate that up to 60% of individuals with atopic dermatitis experience symptoms before the age of one, and 90% by age five.
The condition often persists into adulthood, with about 50% of affected children continuing to have symptoms as adults. Spongiotic dermatitis can significantly impact quality of life, contributing to sleep disturbances, social challenges, and increased healthcare costs. According to the National Eczema Association, annual treatment costs in the U.S. exceed $5.3 billion.
Common Symptoms
The symptoms of spongiotic dermatitis can range from mild to severe and typically include:
- Red, inflamed skin: A hallmark of the condition, often accompanied by itching.
- Blisters or vesicles: Small, fluid-filled bumps that may ooze and crust over.
- Thickened, scaly skin: Chronic cases can lead to lichenification, where the skin becomes thickened and leathery.
- Dryness and cracking: Affected areas may become extremely dry and prone to cracking.
- Intense itching: This can be severe and persistent, leading to scratching and further skin damage.
When to See a Doctor for Spongiotic Dermatitis
Recognizing when to see a doctor for spongiotic dermatitis is essential in preventing the condition from worsening and ensuring effective treatment.
Here are key indicators that warrant medical attention:
1. Persistent or Severe Symptoms
If you experience persistent symptoms that do not improve with over-the-counter treatments or home remedies, it\'s time to seek medical advice. Chronic, severe itching, extensive redness, and discomfort are signs that professional intervention may be needed. A healthcare provider can prescribe stronger topical or systemic medications to alleviate symptoms and reduce inflammation.
2. Infection Signs
One of the most critical times to see a doctor for spongiotic dermatitis is when there are signs of infection. Symptoms of an infected eczema patch include increased redness, warmth, swelling, pus, and pain.
Additionally, red streaks extending from the affected area or a fever may indicate a spreading infection. In such cases, prompt medical attention is crucial to prevent complications.
3. Worsening Symptoms Despite Treatment
When to see a doctor for spongiotic dermatitis also includes situations where symptoms worsen despite following prescribed treatments. If your condition continues to deteriorate or new symptoms emerge, a healthcare provider can reassess your treatment plan and potentially conduct further testing to identify any underlying issues.
4. Impact on Daily Life
Severe spongiotic dermatitis can significantly impact your daily activities, sleep, and overall quality of life. If the condition is affecting your ability to perform daily tasks, concentrate at work or school, or if it causes emotional distress, it is essential to seek medical advice. A doctor can help develop a comprehensive management plan to improve your quality of life.
5. Widespread Eczema
When spongiotic dermatitis covers a large portion of your body, it can be challenging to manage with over-the-counter treatments alone. Extensive eczema requires professional evaluation and possibly systemic treatments, such as oral medications or phototherapy, to control the widespread inflammation effectively.
Preparing for Doctor\'s Visit
When you decide it\'s time to see a doctor for spongiotic dermatitis, being prepared can help ensure a productive visit.
Here are some tips:
- Document Symptoms: Keep a diary of your symptoms, including their severity, duration, and any potential triggers. This data can assist your physician in establishing a precise diagnosis and formulating an efficient treatment strategy..
- List Treatments Tried: Note any over-the-counter treatments or home remedies you have tried and their effects. This can provide valuable insights into what has or hasn\'t worked for you.
- Prepare Questions: Write down any questions or concerns you have about your condition and treatment options. This ensures you address all your concerns during the visit.
- Bring Medical History: Share your medical history, including any other conditions you have and medications you are taking. This helps your doctor consider any potential interactions or contraindications.
Exploring Treatment Options
Upon deciding when to see a doctor for spongiotic dermatitis, your healthcare provider may recommend various treatment options based on the severity and type of dermatitis.
These may include:
- Topical Corticosteroids: Commonly prescribed to reduce inflammation and alleviate itching.
- Topical Calcineurin Inhibitors: Non-steroidal medications that help control inflammation.
- Moisturizers and Emollients: Essential for maintaining skin hydration and barrier function.
- Antibiotics: If there is an infection, oral or topical antibiotics may be necessary.
- Antihistamines: To relieve severe itching and improve sleep.
- Phototherapy: Exposure to specific wavelengths of light to reduce inflammation.
- Systemic Medications: For severe cases, oral or injectable medications that suppress the immune system may be required.
Preventive Measures
While knowing when to see a doctor for spongiotic dermatitis is crucial, preventive measures can also play a significant role in managing the condition. These include:
- Identifying Triggers: Recognize and avoid triggers such as allergens, irritants, and stress that can exacerbate symptoms.
- Skin Care Routine: Establish a gentle skincare routine with regular moisturizing to keep the skin barrier intact.
- Healthy Lifestyle: Promote healthy skin by adhering to a well-rounded diet, ensuring adequate hydration, and effectively managing stress levels.
- Protective Clothing: Wear soft, breathable fabrics and avoid rough materials that can irritate the skin.
Conclusion
Understanding when to see a doctor for spongiotic dermatitis is vital in managing the condition effectively. Persistent, severe, or worsening symptoms, signs of infection, and significant impacts on daily life are clear indicators that professional medical advice is needed.
By seeking timely intervention and following a comprehensive treatment plan, individuals with spongiotic dermatitis can achieve better symptom control and improved quality of life.
Don\'t hesitate to consult a healthcare provider if you are struggling with this condition; they are there to help you navigate and manage your journey to healthier skin.