While upgrading IT infrastructures, businesses are piling up different kinds of old computers, servers, mobile devices, and peripherals at a rapid rate. Total recycling of these devices may seem to be a good environmental practice, but it is also the main cause of data security breaches.
In fact, more than 40% of companies in India had their data leaked in 2025 due to ill-disposed electronic waste. This states that old devices can be hidden sources of vulnerabilities.
Also, improper disposal of electronic waste can result in the leakage of confidential information of the company, which, in turn, may include the details of customers, financial records, patents, and system credential information. Therefore, it is important to hire skilled e-waste recycling services expert.
So, keep reading to find out the reasons behind the data safety necessity, the storage location, the most reliable destruction method and how the expert can help.
Why E-Waste Disposal Can Expose Your Sensitive Data
Electronic gadgets have the capability to store a lot more information than what is perceived by various companies. Quite often, the misconception that deleting files or formatting hard drives is sufficient prevails. In reality, data recovery tools can still retrieve data from improperly discarded devices.
Some of the major risks are:
- Personal And Financial Data: Employees’ personal information, payroll details, and company financial records.
- Intellectual Property: Software, designs, or research that has been developed by the company and can be stolen by competitors for their own benefit.
- Login Credentials And Network Information: Passwords or system access that can lead to unauthorized access.
- Client And Partner Information: Contracts, emails, and other sensitive communications.
If organizations fail to take measures to secure their electronic waste, they are putting themselves in a position where they can become victims of identity theft, fraud, and reputational damage. As a result, e-waste disposal is not only a matter of concern for the environment, but it also forms a vital part of business security.
Where Sensitive Information Lives Inside Old Devices
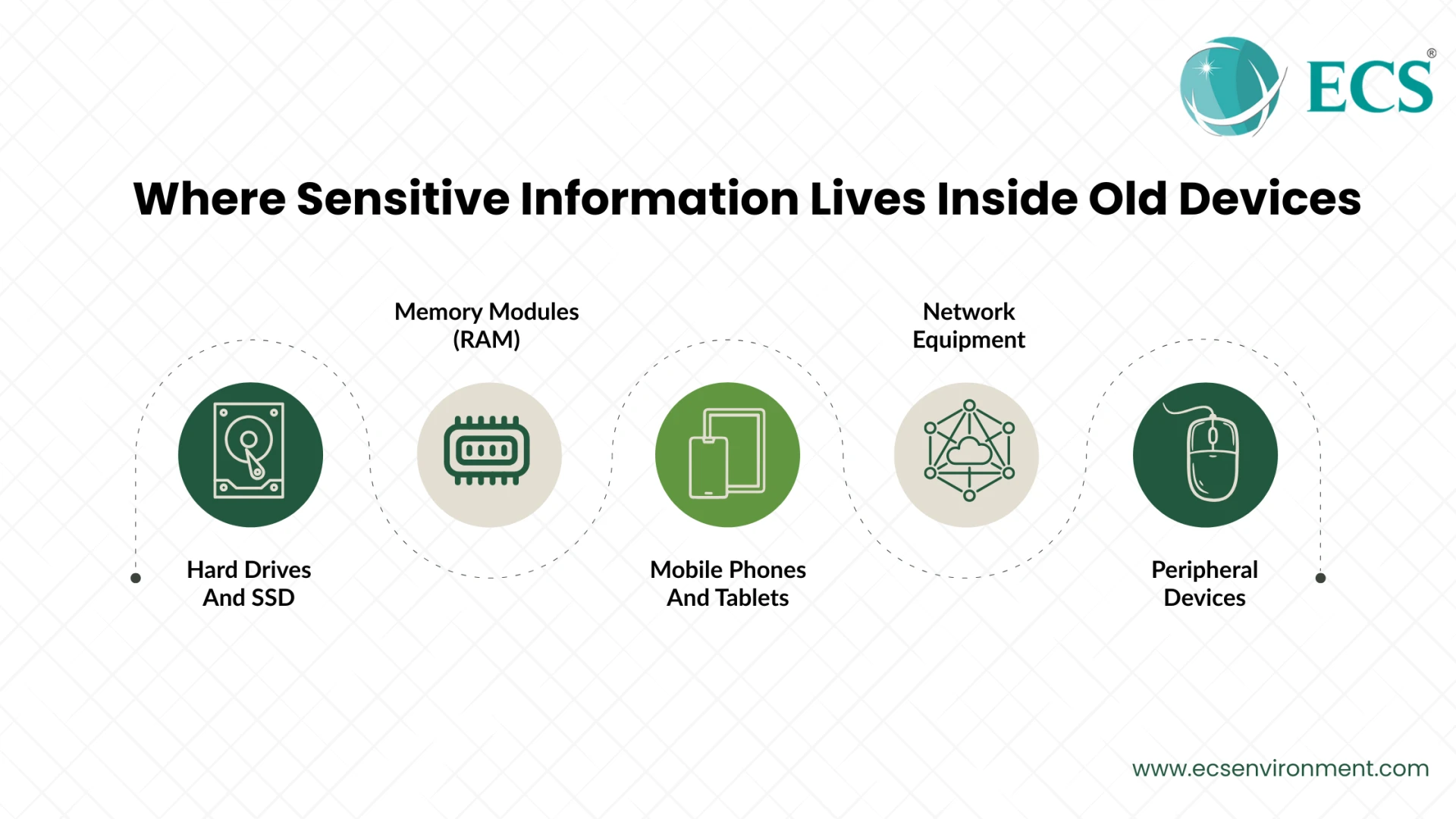
Confidential data can be distributed across various locations on your electronic devices. The knowledge of these places of storage is a great advance towards complete security:
- Hard Drives And SSDs: In these units, operating systems, user files, and application data are stored.
- Memory Modules (RAM): In some instances, remnant data might be left in case where the memory is not wiped out completely.
- Mobile Phones And Tablets: The most common sources of personal and professional information are apps, messages, emails, and contact lists.
- Network Equipment: Routers, firewalls, and switches may have passwords or keys in their configuration files.
- Peripheral Devices: Printers, scanners, and copiers may contain information remnants of any of the documents, whether help or documents, that were either cached or printed.
Unless you take into consideration all these places, there is a risk that your company will be at risk when recycling certain devices.
How Data Theft Happens During E-Waste Recycling
Information theft may be conducted in stages, and the company is usually unaware of it:
- During collection: If the transport is unsecured or the collection services are uncertified, there might be unauthorized individuals who can access the devices.
- On the road: If the devices are transported without the proper chain of custody, they can be stolen.
- At recycling facilities: Some less-than-ethical recyclers may take the components that they have not properly destroyed and reuse them, even though they still contain data.
As a matter of fact, the 2024 report revealed that several hard drives from e-waste in Bangalore were recovered and later resold in the black market. This act led to identity theft and data misuse. Such situations demonstrate the importance of implementing the correct e-waste recycling methods together with strong data protection measures.
Essential Steps to Secure Data Before Hardware Leaves Your Premises
Businesses need to follow a well-organized data protection plan prior to recycling:
- Inventory Management: Recognize all the devices in which critical or sensitive data is stored.
- Data Backup: Take necessary files and back them up in a secure way to avoid accidental loss.
- Certified Data Wiping: Employ the most advanced software from the industry to overwrite data multiple times so that it cannot be recovered.
- Physical Destruction: It may be necessary to hard drive and other storage media pieces to be shredded or degaussed for total security.
- Documentation: Writing down in detail the devices that have been destroyed or wiped for compliance and auditing purposes.
By executing these measures, companies lessen their risk of exposure and meet the requirements of regulatory and industry standards.
Approved Data Destruction Methods for Safe Recycling
Professional recycling electronic waste operations depend on established techniques to guarantee that no data can be retrieved from the devices:
- Degaussing: It uses magnetic fields to make the data on magnetic storage devices unreadable.
- Shredding: Helps physically tearing a hard drive, SSD, or any other kind of storage device into pieces.
- Certified software wiping: It involves complicated patterns like DoD 5220.22-M, which overwrite the data multiple times.
- Incineration: It is a method used for devices that cannot be disassembled in a safe manner by other methods.
Further, with the right e-waste recycling consultation, the selection of the destruction methods will ensure that the sensitive information cannot be recovered, even by very skilled attackers.
The Role of Certified E-Waste Recyclers in Protecting Your Information
Certified e-waste recycling partners add both safety and environmental compliance to the disposal process. Some of the major benefits are :
- ISO-Certified Processes: Help in safe handling and data destruction.
- Secure Chain-Of-Custody: Ensures the safety of devices from collection to the final recycling.
- Audit And Documentation: Gives certificates of data destruction for legal compliance.
- Environmentally Responsible Disposal: Reduces the environmental impact of e-waste.
Recyclers who give e-waste recycling collection services are the ones who provide the security that the devices are disposed of in a safe and socially responsible manner, thus minimizing both environmental and business risks.
Verification: How to Confirm Your Data Is Actually Destroyed
Verification is an indispensable action that supports the prevention of undesired effects that might occur later on:
- Certificates Of Destruction: A formal record that verifies secure data erasure or destruction.
- On-Site Audits: Give companies the opportunity to see for themselves the destruction processes.
- Random Sampling: Makes sure that there is no data that can be retrieved from the devices that have been destroyed.
Besides improving security, this kind of confirmation also helps in the trust-building process between the company and its clients, as well as the regulators.
Common Mistakes Businesses Make When Recycling Old Tech
Even organizations that are knowledgeable about the matter can be prone to making mistakes, which may lead to the exposure of their sensitive data:
- Believing That Mere Deletion Of Files Is Enough: A normal deletion does not permanently remove the data.
- Using uncertified recyclers: Recycling with uncertified recyclers can lead to the illegal resale of storage components.
- Disregarding Mobile Devices And Peripherals: Phones, tablets, printers, and copiers are quite likely to have been loaded with critical data.
- No Documentation: The absence of records may cause compliance failures and even legal issues.
Best Practices to Safeguard Data During E-Waste Recycling
To ensure maximum security:
- Before the disposal, take stock of all devices.
- Recyclers should be reputable and certified, and their procedures must be verified.
- Data destruction methods that are employed must be the ones that are suitable for the given storage.
- To be able to meet the requirements, it is necessary to keep detailed records and certificates of the destruction that has taken place.
- Regular employee training sessions on the importance of e-waste security should be held.
By doing so, one secures the recycling process from any kind of risks, thus sensitive data are safe, and environmental goals are also supported.
Conclusion
Recycling of e-waste is extremely significant to the earth and in terms of cybersecurity. To ensure that there is no risk of data leak, the companies should verify that they have undertaken all the necessary steps to make sure that there is nothing left to be done,. This includes checking that the data destruction methods used are certified that through a right e- waste recycling company in Bangalore, Hyderabad or from any other IT city.
With secure e-waste recycling procedures and proper management, the companies will be in a position to avoid data breaches, reduce the threat of violation of the rules and regulations, and help in protecting the planet.
Here ECS, one of the best e-waste recycling company in Hyderabad or Bangalore will help you find reliable solutions to help you protect your company data. Our certified e-waste recycling expert will ensure that your devices dismantled safely and recycled in an environmentally friendly way.
Get in touch with them them today so that you can dispose of of your e-waste in a manner that will never make your sensitive information insecure.
FAQ
1. What Do E-Waste Recycling Services Mean?
E-waste recycling services refer to those services that not only are involved with the safe disposal of old electronic equipment. But in the some way, they are also environmentally friendly, as well as providing data destruction.
2. What Is The Vision Of Data Security In The E-Waste Recycling Process?
In case of improper disposal, it might also expose the most valuable business, financial, or personal information to hackers without the knowledge of the owners.
3. What Can Businesses Do To Ensure That They Have Destroyed Data?
On the one hand, it has certificates of destruction. Secondly, there exist on-site audits. Thirdly, the sampling of the devices can be done randomly.
4. Which Devices Are To Be Included In The E-Waste Recycling?
Computers, servers, laptops, tablets, smartphones, and networking devices that have stored sensitive information.
5. What Do The Certified Recyclers Do To Protect Information?
They use safe data destruction practices, a a chain of custody, and provide compliance.



