Capacitive touch technology is a method of detecting and responding to human touch by measuring changes in electrical charge. Unlike traditional mechanical switches or resistive touch systems, it requires no pressure, just a light touch from a conductive object like a finger.
This makes it ideal for creating sleek, responsive, and durable interfaces across a wide range of electronic devices.
What Is Capacitive Touch Technology?
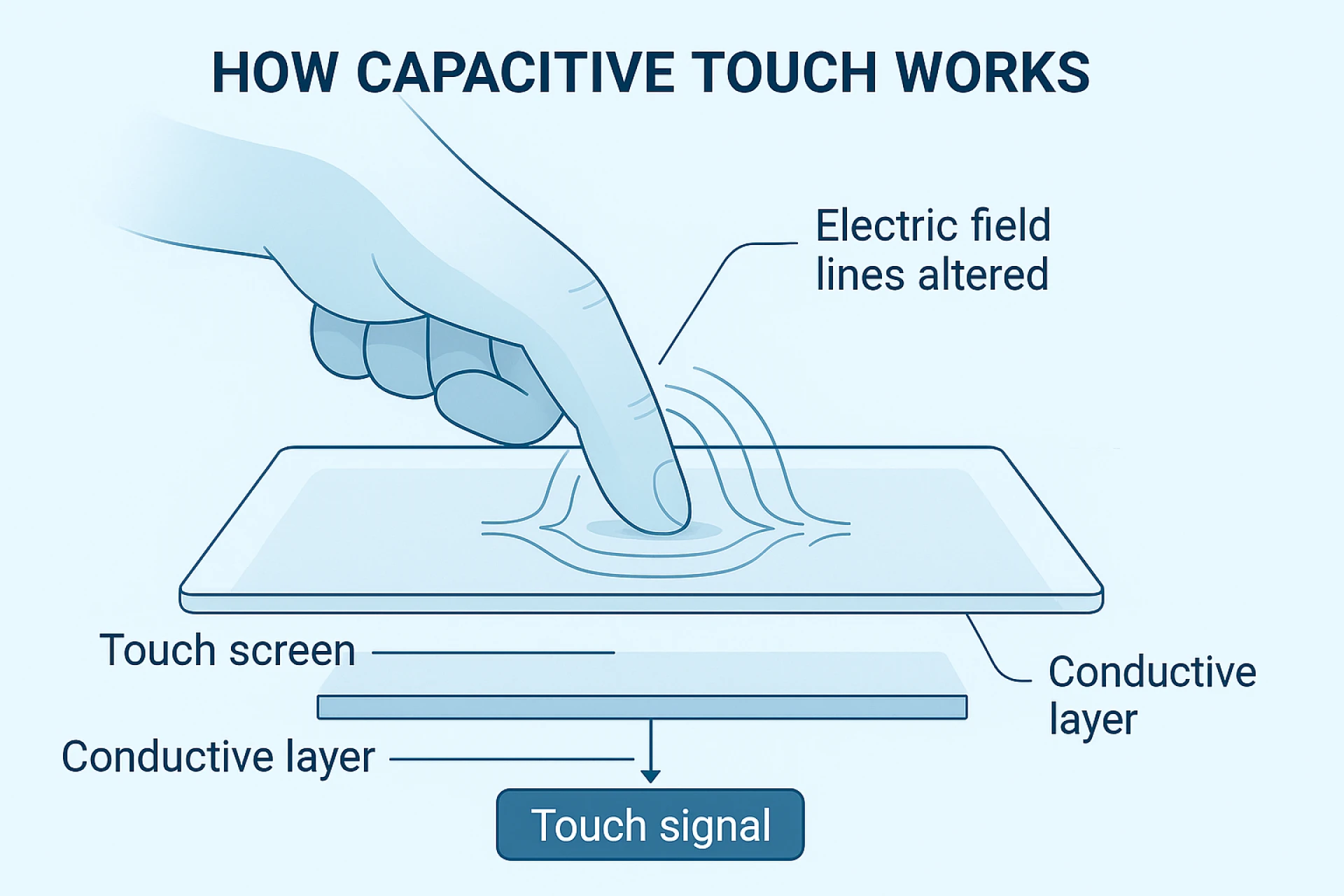
Capacitive touch technology enables seamless interaction with modern electronic devices. It operates by detecting subtle changes in electrical charge across a conductive layer beneath a screen’s surface.
When a finger or conductive object makes contact, it alters the localized electrical field, allowing the system to pinpoint the touch location with high accuracy. This touch input method is quick, does not require pressure, and is highly responsive, making it ideal for today’s intuitive user interfaces.
Unlike resistive screens that rely on physical pressure, capacitive touch screens offer better durability, clarity, and user experience. Their ability to detect multiple touch points also supports modern gestures like swiping, zooming, and rotating, which are essential for smooth digital interaction in various settings.
Types of Capacitive Touch Technology
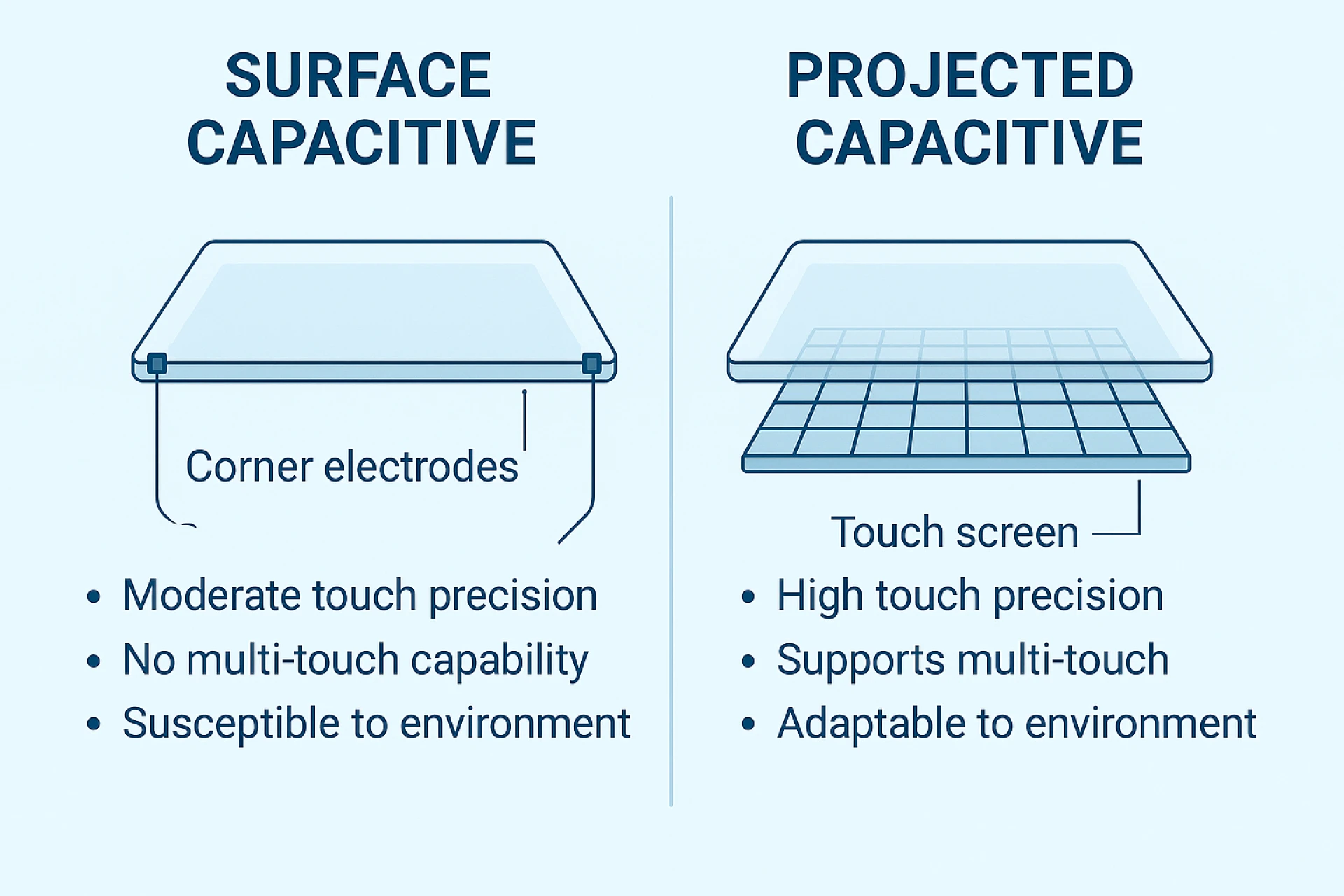
1. Surface Capacitive
This type involves a single conductive layer with electrodes at each corner of the screen. A uniform voltage is applied, and when touched, a small current is drawn, which varies based on the position of the touch. The controller calculates the touch point based on these changes.
- Durability: Surface capacitive screens are encased in glass, making them highly resistant to scratches and impacts.
- Optical Clarity: The absence of multiple layers helps maintain high display clarity.
- Single-Touch Limitation: These screens are limited to one-touch inputs and cannot support complex gestures.
2. Projected Capacitive (PCAP)
Projected capacitive technology consists of a matrix of conductive electrodes arranged in rows and columns beneath the screen. When a finger comes close, it alters the mutual capacitance at those grid intersections. This system enables the precise detection of multiple touch points simultaneously.
- Multi-Touch Capability: Supports advanced gestures including pinch-to-zoom, rotate, and swipe.
- Environmental Flexibility: Works reliably through protective layers, gloves, and even under water-resistant coatings.
- Application Range: Used in smartphones, tablets, medical devices, industrial panels, and automotive interfaces.
For a detailed comparison between capacitive and resistive touch technologies, read this guide on Capacitive vs Resistive Touch Screen.
Real-World Applications of Capacitive Touch
1. Consumer Electronics
Capacitive touch technology is the standard in smartphones, tablets, laptops, and smart home devices.
- User-Friendly Interfaces: Easy navigation through apps, photos, and settings.
- Advanced Gestures: Enables fast and intuitive control through multi-touch gestures.
- Design Aesthetics: Allows for bezel-less, edge-to-edge screens and modern, minimalist designs.
2. Medical Equipment
Healthcare devices such as diagnostic monitors, infusion pumps, and surgical systems use capacitive touch panels.
- Glove Compatibility: Operates reliably through medical gloves made from nitrile, latex, or vinyl.
- Hygienic Surfaces: Easy-to-clean glass ensures infection control and patient safety.
- Integrated Data Access: Enables clinicians to interact directly with patient records, settings, and test results.
3. Automotive Interfaces
Capacitive touch is increasingly used in infotainment systems, navigation controls, and climate panels.
- Driver Safety: Supports gestures that minimize distraction, such as swiping to change music or map views.
- Environmental Endurance: Withstands vibration, temperature changes, and high humidity.
- Customization: Offers configurable layouts for different car models and trim levels.
For a deeper look at automotive use cases, explore how capacitive touch is advancing vehicle interfaces.
4. Industrial Human-Machine Interfaces
In industrial environments, capacitive touch screens are used in control systems and rugged handheld devices.
- Ingress Protection: Many screens meet IP65 or IP67 standards for dust and water resistance.
- Long Lifespan: Designed for millions of actuations, reducing downtime and maintenance.
- Touch Accuracy: Maintains functionality even when operators wear protective gloves or the panel is wet.
Key Innovations and Advancements
1. Transparent and Flexible Electrodes
New conductive materials like silver nanowires, carbon nanotubes, and graphene have replaced traditional ITO layers.
- Flexibility: These materials support bendable and rollable displays.
- Cost Efficiency: Offer simpler, more scalable manufacturing processes.
- High Transparency: Maintain superior image clarity while improving screen thinness.
2. Glove and Moisture Compatibility
Modern capacitive controllers work through gloves and wet conditions.
- Sensitivity Adjustment: Adaptive signal tuning adjusts to glove thickness or environmental interference.
- Moisture Rejection: Algorithms filter out false touches from water droplets or mist.
- Outdoor Readiness: Ideal for public kiosks, ATMs, and outdoor industrial displays.
3. Foldable and Curved Displays
Capacitive sensors are now embedded in flexible OLED panels.
- New Form Factors: Enables foldable smartphones, curved dashboard panels, and wearable bands.
- Enhanced Interaction: Integrates with haptics, stylus input, and voice commands.
- Resilience: Maintains consistent performance after thousands of bends or folds.
Benefits of Capacitive Touch Technology
- High Sensitivity and Accuracy: Capable of detecting very light touches and offering precise input.
- Durability: Solid-state design with glass surfaces makes these screens resistant to wear and tear.
- Multi-Touch Functionality: Allows intuitive control with gestures, improving user interaction.
- Aesthetic Appeal: Enables sleek, modern designs with seamless glass panels.
- Low Maintenance: No mechanical parts reduce the risk of failure or degradation over time.
Challenges of Capacitive Touch Technology
- Cost: Typically more expensive than resistive alternatives due to advanced materials and processing.
- Moisture Sensitivity: May require special controllers or software tuning to reject false signals in humid or wet conditions.
- Glove Incompatibility: Not all gloves work without capacitive-friendly materials unless specifically designed to do so.
- Electromagnetic Interference: Requires noise filtering for reliable operation near power-intensive devices.
Industries That Benefit Most from Capacitive Touch
- Consumer Electronics: Smartphones, tablets, smartwatches, laptops, and smart TVs.
- Medical and Healthcare: Diagnostic tools, surgical monitors, and hospital control panels.
- Automotive: Infotainment systems, dashboards, and vehicle control interfaces.
- Industrial Automation: Factory HMIs, control panels, kiosks, and public terminals.
- Retail and Hospitality: Point-of-sale systems, digital signage, and self-checkout stations.
Looking Forward
Capacitive touch technology is steadily shaping the future of human-machine interaction. Its adaptability, sensitivity, and seamless user experience have made it indispensable across multiple industries.
Continued improvements in sensor technology, materials, and processing algorithms are expanding its functionality in challenging conditions from surgical theaters and manufacturing floors to connected vehicles and smart homes.
Touch screens will soon become even more intuitive, combining voice, haptic, and gesture inputs into cohesive, intelligent systems. Capacitive sensing will be a vital enabler in the next generation of interactive technology, bringing users closer to the devices they depend on every day.