Introduction
In the vast landscape of the internet, seamless and efficient routing is crucial for delivering data across networks. The Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) stands tall as the protocol that glues the internet together, enabling communication between autonomous systems (AS). Cisco Packet Tracer, a powerful network simulation tool, provides an excellent platform to understand and practice BGP configuration in a controlled environment. In this comprehensive blog post, we will explore the significance of BGP in modern networking, learn how to configure BGP on Cisco routers in Packet Tracer, and uncover the benefits of this protocol in achieving reliable and dynamic routing on the internet.
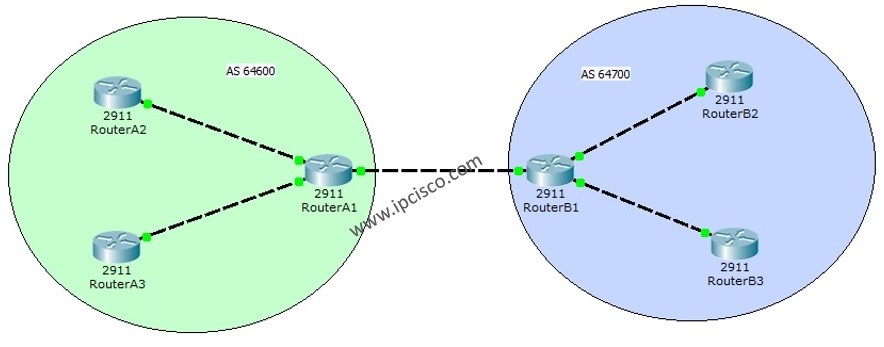
Section 1: Understanding Border Gateway Protocol
Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) is an exterior gateway protocol that operates at the core of the internet, facilitating communication between different autonomous systems. Unlike interior gateway protocols (IGP), BGP is used to exchange routing information between networks belonging to different organizations or ISPs. BGP uses path-vector algorithms to determine the best path for routing data across the internet, considering factors like AS path, network policies, and reachability information. This unique characteristic makes BGP the key protocol behind the internet's inter-domain routing.
Section 2: Configuring BGP on Cisco Routers in Packet Tracer
Step 1: Access the Router CLI In Packet Tracer, access the router's Command Line Interface (CLI) to begin configuring BGP.
Step 2: Enable BGP and Configure Neighbors Enable BGP on the router using the “router bgp [AS-number]” command. Choose the autonomous system number (AS-number) that uniquely identifies the router within the autonomous system. Next, configure the BGP neighbor statement using the “neighbor [neighbor-ip] remote-as [neighbor-AS]” command to establish a peering relationship with neighboring routers.
Step 3: Advertise Networks Use the “network [network-address] mask [network-mask]” command to advertise the local networks that the router should make reachable through BGP.
Step 4: Configure BGP Attributes (Optional) Adjust BGP attributes, such as local preference, MED (multi-exit discriminator), or communities, to influence routing decisions and traffic flow.
Step 5: Verify BGP Configuration Use the “show ip bgp” and “show ip bgp neighbors” commands to verify BGP configuration and view information about BGP neighbors and routing updates.
Section 3: Benefits of BGP Configuration
- Scalable Routing: BGP enables efficient routing across the internet, making it scalable to accommodate the vast number of networks and ASes.
- Dynamic Path Selection: BGP's sophisticated path selection mechanism ensures dynamic routing decisions based on real-time network conditions.
- Redundancy and Resilience: BGP supports multiple paths to the same destination, ensuring redundancy and resilience in case of link failures.
- Policy Control: BGP allows network administrators to define routing policies, influencing the path selection and optimizing traffic flow.
Section 4: Practical Implementation of BGP in Packet Tracer
Using Packet Tracer, simulate a network scenario with multiple routers representing different autonomous systems. Configure BGP on the routers, establishing peerings and advertising networks. Observe how BGP dynamically updates routing tables and selects the best paths for data transmission between ASes.
Section 5: Troubleshooting BGP Configuration in Packet Tracer
Common issues when configuring BGP in Packet Tracer include incorrect AS numbers or misconfigured neighbor statements. Troubleshoot these issues by verifying BGP configurations on all routers and ensuring the correct AS numbers and IP addresses.
Section 6: Conclusion
Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) is the backbone of the internet, playing a pivotal role in inter-domain routing. In Cisco Packet Tracer, network enthusiasts, students, and professionals can practice BGP configurations to gain valuable hands-on experience with this essential networking protocol. BGP's dynamic path selection, scalability, and policy control make it indispensable for internet routing. Embrace BGP configuration in Packet Tracer to elevate your networking skills and gain insights into the intricacies of inter-domain routing, empowering your organization with reliable and efficient data transmission across the global internet.




