Psoriasis Disease Overview:
Psoriasis Disease is a chronic autoimmune skin condition that affects millions of people worldwide. In this article, we will explore Psoriasis disease, covering key aspects such as the global death rate due to Psoriasis, diagnostic analysis, treatment options, emerging therapies, the regulatory framework, competitive landscape, market trends, and clinical data assessment. By the end of this article, you will have a well-rounded understanding of Psoriasis and the evolving landscape surrounding it.
Psoriasis Disease Symptoms:
Psoriasis Disease is a chronic skin condition that can manifest in various ways, and its symptoms can range from mild to severe. The most common Symptoms of psoriasis include:
- Red, Inflamed Skin: Psoriasis often causes patches of red, inflamed skin. The affected areas may be covered with silvery-white scales.
- Thick, Silvery Scales: These scales can develop on top of the red, inflamed patches of skin. They often look silvery or whitish and can be dry and easily shed.
- Itching and Discomfort: Psoriasis can be itchy and, in some cases, even painful. Scratching the affected areas can lead to further irritation and may trigger a condition called the Koebner phenomenon, where new psoriasis plaques form at the site of skin injury.
- Dry, Cracked Skin: The skin affected by psoriasis is often dry and may crack, leading to bleeding in some cases.
- Bleeding: In severe cases, the skin may become so dry and cracked that it bleeds.
- Nail Changes: Psoriasis can affect the nails, causing pitting (small dents or depressions), thickening, discoloration, and in some cases, separation of the nail from the nail bed.
- Joint Pain: Some people with psoriasis may develop a type of arthritis called psoriatic arthritis. This condition can cause joint pain, stiffness, and swelling.
- Scalp Psoriasis: Psoriasis can affect the scalp, leading to red, scaly patches or a more widespread rash. It can also cause itching and flaking.
- Inverse Psoriasis: This type of psoriasis appears as smooth, red, inflamed patches in skin folds, such as under the breasts, in the armpits, or in the groin area.
- Guttate Psoriasis: This type often appears as small, dot-like lesions on the skin. It's typically triggered by a bacterial or viral infection.
- Pustular Psoriasis: In this form, pustules (blisters filled with pus) may develop on the red skin. It can be localized or widespread.
- Erythrodermic Psoriasis: This is a severe and rare form of psoriasis where the skin becomes red, peels, and may be very itchy and painful. It can cover large areas of the body.
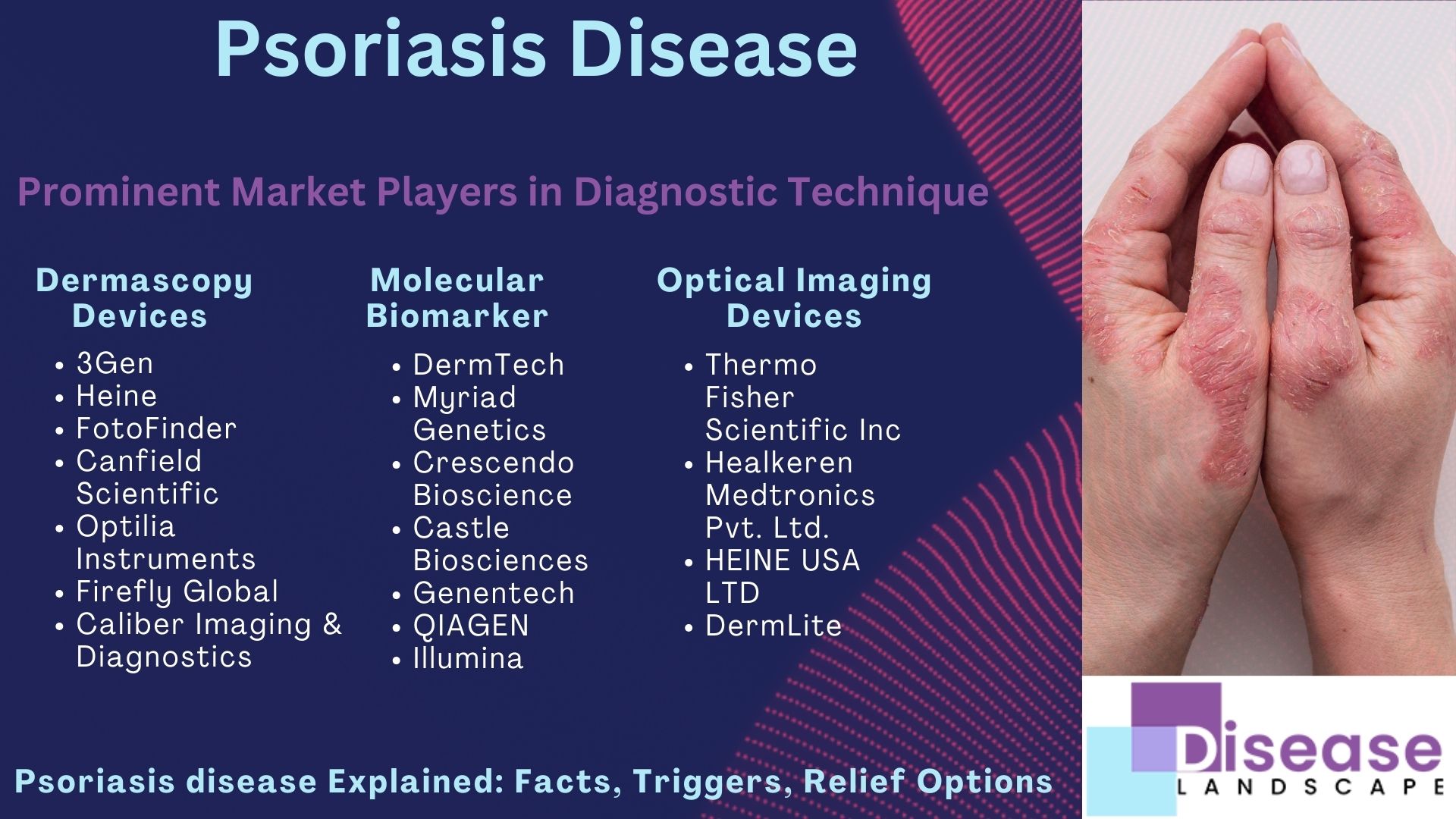
The Psoriasis Disease Market Competitors Listed Below are Revolutionizing Healthcare with Innovative Diagnostic Inventions:
Dermascopy Devices:
- 3Gen
- Heine
- FotoFinder
- Canfield Scientific
- Optilia Instruments
- Firefly Global
- Caliber Imaging & Diagnostics
Molecular Biomarker:
- DermTech
- Myriad Genetics
- Crescendo Bioscience
- Castle Biosciences
- Genentech
- QIAGEN
- Illumina
Optical Imaging Devices:
- Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc
- Healkeren Medtronics Pvt. Ltd.
- HEINE USA LTD
- DermLite
Browse In-depth Research Report on Psoriasis Disease:
https://www.diseaselandscape.com/autoimmune/psoriasis-disease-signs-symptoms
Diagnostic Analysis:
Diagnosing Psoriasis typically relies on clinical assessment. Dermatologists examine the affected skin areas, looking for telltale signs such as red, scaly patches and silvery scales. In challenging cases, a skin biopsy may be necessary for a definitive diagnosis. Additionally, medical history and family history play crucial roles in understanding a patient's predisposition to Psoriasis.
Treatment Analysis:
While Psoriasis is a lifelong condition with no cure, several treatment options are available to manage its symptoms. These include topical treatments like corticosteroids and vitamin D analogs, phototherapy, and systemic treatments like oral medications and biologics. The choice of treatment depends on the severity of the condition and individual patient factors.
New Therapies in Development:
The field of Psoriasis research is dynamic, with several promising therapies in various stages of development. These therapies aim to provide more effective and targeted treatments with fewer side effects. Biologics, which target specific components of the immune system, have revolutionized Psoriasis treatment and continue to evolve.
Regulatory Framework:
The regulatory landscape for Psoriasis treatments varies by region, but most treatments undergo rigorous testing and approval processes to ensure safety and efficacy. Government agencies such as the FDA in the United States and the EMA in Europe play a critical role in evaluating and approving Psoriasis medications.
Competitive Analysis:
The Psoriasis treatment market is competitive, with numerous pharmaceutical companies and biotechnology firms striving to develop innovative therapies. Key players in this market include AbbVie, Novartis, Johnson & Johnson, and Amgen. Competition has led to the development of diverse treatment options, enhancing patient choices.
Market Trends Analysis:
The Psoriasis treatment market is experiencing several notable trends, including:
- Personalized Medicine: Tailoring treatments to an individual's specific Psoriasis type and severity.
- Emerging Biologics: The continuous development of biologics offering improved effectiveness and convenience.
- Telehealth: The rise of telemedicine, making it easier for Psoriasis patients to access specialist care remotely.
Clinical Data Assessment:
Clinical trials play a pivotal role in advancing Psoriasis treatments. Through rigorous testing, researchers gain insights into treatment safety, efficacy, and potential side effects. Patients can contribute to the advancement of Psoriasis care by participating in clinical trials, helping to refine existing treatments and develop new ones.
Conclusion:
Psoriasis is a chronic condition that requires comprehensive management to mitigate its impact on the lives of those affected. While it may not directly result in high mortality rates, the physical and emotional toll it takes is significant. Advances in diagnostic tools, treatments, and ongoing research provide hope for improved care and the potential for a better quality of life for Psoriasis patients. As the field of Psoriasis management continues to evolve, staying informed about the latest developments is essential for patients and healthcare professionals alike.
Browse Through More Autoimmune Diseases Research Reports:
For More Related Reports:
Understanding Crohn's Disease: Its Causes, Signs, and Treatment
Revolutionizing Parkinson's Disease Care: Global Insights and Innovations
Unlocking the Latest Breakthroughs in Alzheimer's Disease Research: Hope on the Horizon
Rising Against the Odds: Global Insights into Multiple System Atrophy (MSA) Disease