Introduction:
In recent years, there has been a growing interest in alternative therapies for mental health conditions. One such therapy that has gained significant attention is Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS). TMS offers a non-invasive and promising approach to treat various psychiatric and neurological disorders. In this blog post, we will delve into the world of TMS therapy, exploring its mechanism, applications, and potential benefits.
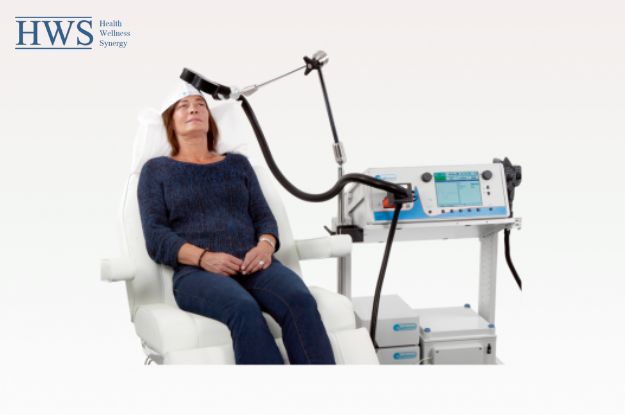
Understanding TMS Therapy:
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation therapy involves the use of magnetic fields to stimulate specific areas of the brain. It works by placing an electromagnetic coil against the scalp, which generates focused magnetic pulses. These pulses induce electrical currents in the targeted brain regions, modulating neural activity and promoting beneficial changes.
Applications of TMS Therapy:
Depression:
TMS therapy has been particularly effective in treating major depressive disorder (MDD). For individuals who have not responded adequately to antidepressant medications, TMS therapy offers a viable alternative. It has shown promising results in alleviating depressive symptoms, improving mood, and enhancing overall well-being.
Anxiety Disorders:
TMS therapy has also demonstrated potential in the treatment of anxiety disorders, including generalized anxiety disorder (GAD), post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), and obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD). By regulating neural circuits associated with anxiety, TMS therapy can help reduce anxiety symptoms and restore a sense of calm.
Neurological Conditions:
TMS therapy is not limited to mental health disorders alone. It has shown efficacy in various neurological conditions such as migraine headaches and chronic pain. By targeting specific brain regions involved in pain processing, TMS therapy can provide relief and improve the quality of life for individuals suffering from chronic pain.
Benefits of TMS Therapy:
Non-invasiveness:
Unlike other brain stimulation techniques, TMS therapy is non-invasive, meaning it does not require surgery or anesthesia. This reduces the associated risks and allows for a more comfortable treatment experience.
Minimal Side Effects:
TMS therapy is generally well-tolerated, with minimal side effects. Some individuals may experience mild scalp discomfort or headaches during or after the session, but these effects are typically temporary and subside quickly.
Personalized Treatment:
TMS therapy can be tailored to the specific needs of each individual. The treatment parameters, such as intensity, frequency, and duration, can be adjusted to optimize outcomes and accommodate individual responses.
Adjunct to Other Treatments:
TMS therapy can be used in combination with other treatment modalities, including medication and psychotherapy, to enhance overall efficacy. It offers a complementary approach that may improve treatment outcomes when used in conjunction with traditional interventions.
Conclusion:
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) therapy represents a promising frontier in mental health and neurological treatments. Its non-invasive nature, minimal side effects, and broad applications make it an attractive option for individuals who have not responded well to traditional therapies. TMS therapy has the potential to transform the lives of those suffering from depression, anxiety disorders, and other neurological conditions. As research and advancements in TMS technology continue, we can expect further refinements and a deeper understanding of its therapeutic potential. With its ability to stimulate and modulate brain activity, TMS therapy offers hope and opens new doors to mental wellness and neurological recovery.