The Class 9 Notes on Matter in Our Surroundings – This section contains summary and revision notes for the Class 9 Science chapter 1. This CBSE notes includes CBSE Key Nots, CBSE Rev Notes, short Key Notes as well as images and diagrams for the complete Chapter 1 titled “Matter in Our Surroundings” of Science that was taught in class 9. NCERT Textbook is used to teach Science to class 9. Chapter 1 Matter in our Surroundings must be read. You will want to review the lesson and then find notes that you can remember. You can find complete Chapter 1 Matter In Our Surroundings 9 notes here. You should also see Class 12 English book.
CBSE Class 9, Science Notes Chapter 1, Matter in Our Surroundings
Facts that Matter
Introduction
-
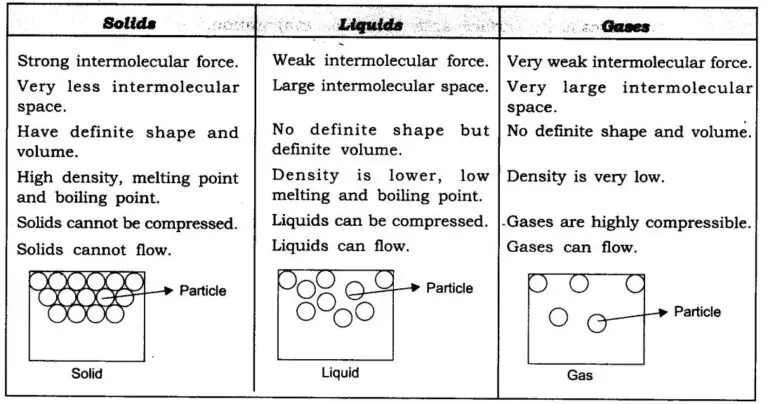
Everything in this universe is made from materials scientists have called'matter.
-
The matter is made of tiny particles. It is not continuous, but particulate.
-
Matter refers to anything that occupies space, and has mass.
-
Matter particles are always moving because they have space between them.
-
Particles of matter attract one another.
States of Matter: It has three states.
Matter can change from solid to fluid, liquid to gas or vice versa. You can also download PDF of Class 11 Maths NCERT book .
Temperature effect: As heat increases, particles are able to gain energy and vibrate more efficiently. A new state can be achieved when the particles have more kinetic energy.
The melting point is the temperature at what a solid melts to make it a liquid at atmospheric pressure.
Boiling Point: A liquid's boiling point is the temperature at its point of boiling at atmospheric pressure. Boiling refers to a bulk phenomenon.
Latent heat or fusion: This refers to the heat required to convert 1 kg of a solid from liquid at its melting point into liquid.
Latent heat or vaporization: At atmospheric pressure, the heat energy required for 1 kg liquid to become vapour is known as the latent heat.
Pressure change can affect the matter. By applying pressure, particles of matter are brought closer together and the matter's state can be modified. You can solidify CO2 gas by using pressure and decreasing temperature.
Evaporation is the process of changing a liquid from liquid to vapour at temperatures below its boiling temperature. Evaporation is a top phenomenon.
Factors affecting evaporation.
-
Evaporation increases with an increase in the surface area.
-
Temperature increases will increase the rate at which evaporation occurs.
-
A decrease in humidity will increase the rate at which evaporation occurs.
-
A rise in wind speed will increase the rate at which evaporation occurs.
-
Evaporation produces a cooling effect.
Some quantifiable quantities and their units