Virtual Data Optimizer (VDO) is a device mapper module which provides data reduction capabilities to the Linux block storage stack. It uses deduplication and inline compression features to shrink data as it is being written to storage media.
VDO optimizes the data on block devices by reducing disk space usage on block devices, and minimizing the replication, saving disk space and increasing data throughput. VDO includes two kernel modules:
Why does VDO matter?
VDO can be used to save storage and reduce costs. Because it’s a feature of Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL), it can be used either in traditional datacenter or in cloud based environment
In the traditional data center, VDO can repurpose storage resources already have and make efficient use of future equipment. Enterprise data replication can also benefit from this efficiency, since fewer data on storage means less data to replicate.
In the cloud, VDO allows cutting storage costs as well. Depending on deployment needs, this can translate to lower costs per compute instance, lower costs for cloud-based storage, and reduced costs for long-term retention of data snapshots. Reduced footprint on premises or in the cloud will reduce the bandwidth requirements for data transfer to or from the cloud or even between clouds.
Features of VDO
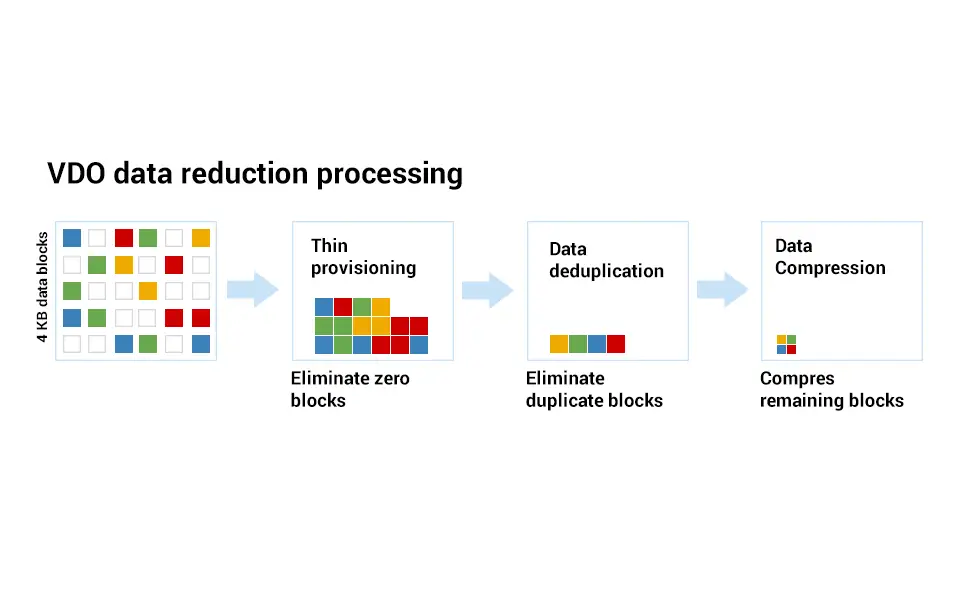
Zero-Block Elimination: VDO filters out data blocks that contain only zeroes (0) and records the information of those blocks only in the metadata. The nonzero data blocks are then passed to the next stage of processing. This stage applies the thin provisioning feature in the VDO devices.
Deduplication eliminates redundant data blocks. When we create multiple copies of the same data, VDO identify the duplicate data blocks and directs the metadata to use those duplicate blocks as references to the original data block without creating duplicate blocks. The UDS kernel module checks data redundancy through the metadata it maintains. This kernel module ships as part of the VDO.
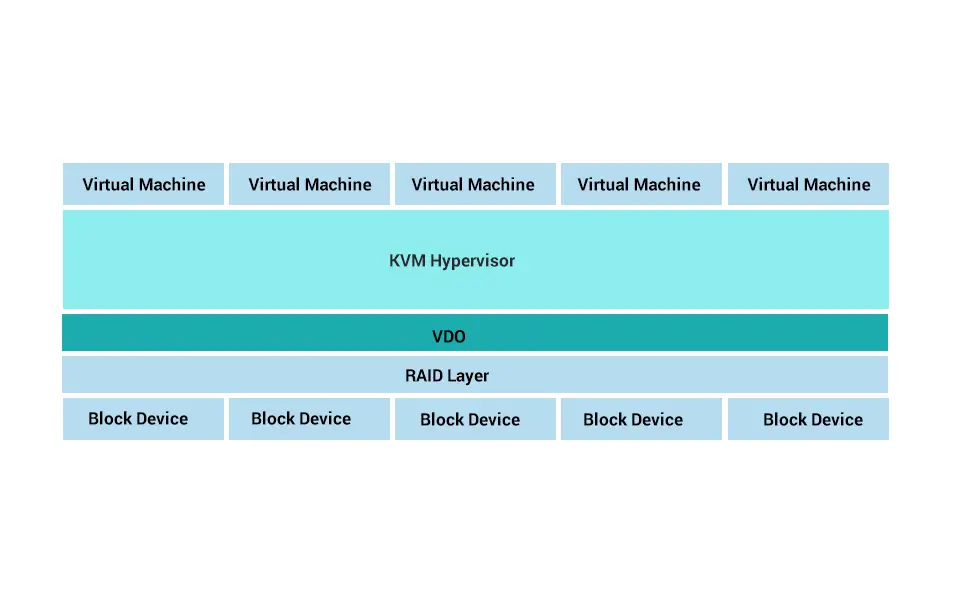
VDO Features
Compression: LZ4 compression is applied to the data blocks after the zero block elimination and deduplication phases are completed. The compressed data blocks are packed together into 4 KB blocks and stored on media. A single physical block can accommodate more compressed blocks; this can speed up the performance for reading data off storage.
To get enough knowledge related to this topic, there is various Linux server administration training in Kochi to lead you into the right path of learning. The best lessons and skills are driven from courses of the best solutions. Hence, with Linux Server administration courses in Kochi prepare towards the future technology.






